Immune cells-derived exosomes function as a double-edged sword: role in disease progression and their therapeutic applications
- PMID: 35550636
- PMCID: PMC9102350
- DOI: 10.1186/s40364-022-00374-4
Immune cells-derived exosomes function as a double-edged sword: role in disease progression and their therapeutic applications
Abstract
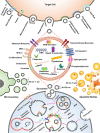
Exosomes, ranging in size from 30 to 150 nm as identified initially via electron microscopy in 1946, are one of the extracellular vesicles (EVs) produced by many cells and have been the subject of many studies; initially, they were considered as cell wastes with the belief that cells produced exosomes to maintain homeostasis. Nowadays, it has been found that EVs secreted by different cells play a vital role in cellular communication and are usually secreted in both physiological and pathological conditions. Due to the presence of different markers and ligands on the surface of exosomes, they have paracrine, endocrine and autocrine effects in some cases. Immune cells, like other cells, can secrete exosomes that interact with surrounding cells via these vesicles. Immune system cells-derived exosomes (IEXs) induce different responses, such as increasing and decreasing the transcription of various genes and regulating cytokine production. This review deliberate the function of innate and acquired immune cells derived exosomes, their role in the pathogenesis of immune diseases, and their therapeutic appliances.
Keywords: Cellular medicine; Exosome; IEXs; Immune cell; Pathogenesis; Therapeutic application.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Logozzi M, Di Raimo R, Mizzoni D, Fais S. What we know on the potential use of exosomes for nanodelivery. In: Seminars in Cancer Biology. Academic Press; 2021. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

