A novel chronic in vivo oral cadmium exposure-washout mouse model for studying cadmium toxicity and complex diabetogenic effects
- PMID: 35550884
- PMCID: PMC9854171
- DOI: 10.1016/j.taap.2022.116057
A novel chronic in vivo oral cadmium exposure-washout mouse model for studying cadmium toxicity and complex diabetogenic effects
Abstract
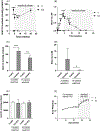
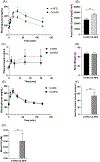
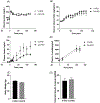
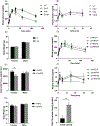
Type II diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is characterized by insulin resistance, β-cell dysfunction and hyperglycemia. In addition to well known risk factors such as lifestyle and genetic risk score, accumulation of environmental toxicants in organs relevant to glucose metabolism is increasingly recognized as additional risk factors for T2DM. Here, we describe the development of an in vivo oral cadmium (Cd) exposure model. It was shown that oral Cd exposure in drinking water followed by washout and high fat diet (HFD) in C57BL/6N mice results in islet Cd bioaccumulation comparable to that found in native human islets while mitigating the anorexic effects of Cd to achieve the same weight gain required to induce insulin resistance as in Cd naïve control mice. Inter individual variation in plasma glucose and insulin levels as well as islet Cd bioaccumulation was observed in both female and male mice. Regression analysis showed an inverse correlation between islet Cd level and plasma insulin following a glucose challenge in males but not in females. This finding highlights the need to account for inter individual target tissue Cd concentrations when interpreting results from in vivo Cd exposure models. No effect of Cd on insulin secretion was observed in islets ex vivo, highlighting differences between in vivo and ex vivo cadmium exposure models. In summary, our oral in vivo Cd exposure-washout with HFD model resulted in islet Cd bioaccumulation that is relevant in the context of environmental cadmium exposure in humans. Here, we showed that islet Cd bioaccumulation is associated with complex cadmium-mediated changes in glucose clearance and β-cell function. The model described here will serve as a useful tool to further examine the relationship between Cd exposure, islet Cd bioaccumulation, dysglycemia and their underlying mechanisms.
Keywords: Cadmium; High fat diet; Insulin; Mouse model; Pancreatic islets; Type II diabetes.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
The authors declare the following financial interests/personal relationships which may be considered as potential competing interests:
Figures

References
-
- Afridi HI, Kazi TG, Kazi N, Jamali MK, Arain MB, Jalbani N, Baig JA and Sarfraz RA (2008). “Evaluation of status of toxic metals in biological samples of diabetes mellitus patients.” Diabetes Res Clin Pract 80(2): 280–288. - PubMed
-
- Antala S and Dempski RE (2012). “The human ZIP4 transporter has two distinct binding affinities and mediates transport of multiple transition metals.” Biochemistry 51(5): 963–973. - PubMed
-
- Arredondo M, Munoz P, Mura CV and Nunez MT (2003). “DMT1, a physiologically relevant apical Cu1+ transporter of intestinal cells.” Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 284(6): C1525–1530. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee M, Vats P, Kushwah AS and Srivastava N (2019). “Interaction of antioxidant gene variants and susceptibility to type 2 diabetes mellitus.” Br J Biomed Sci 76(4): 166–171. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

