Effects of blue-green LED lights with two perceived illuminance (human and poultry) on immune performance and skeletal development of layer chickens
- PMID: 35550997
- PMCID: PMC9108713
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psj.2022.101855
Effects of blue-green LED lights with two perceived illuminance (human and poultry) on immune performance and skeletal development of layer chickens
Abstract
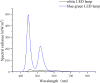
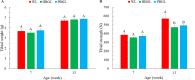
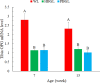
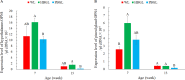
Light is one of the essential environmental factors in the production process of laying hens, which can directly affect their behavior, growth and development, and production performance. The spectral sensitivity of humans is different from that of poultry, and the perceived illuminance units of human and poultry are lux and clux, respectively. If the light management of laying hen production is carried out according to human perceived illuminance, the growth and development of laying hens during pullet rearing may be adversely affected due to the discomfort of the perceived illuminance. Preliminary research has found that blue-green LED light can improve the immune function of laying hens during the brooding and rearing periods. However, the differences of the effects caused by blue-green light on the immune performance and bone development of laying hens during pullet rearing are still unclear for the 2 spectral sensitivities. A total of 120 Jinghong layer chickens were raised from 1 d to 13 wk of age in one of three groups with a white LED light (light intensity unit lux, WL) group, a blue-green LED light (light intensity unit lux, HBGL) group, and blue-green LED light (light intensity unit clux, PBGL) group, and unlimited feed and water were provided during the whole experiment. At 7 and 13 wk of age, the immune performance, bone parameters, and related gene expression were investigated. The results showed that compared with the WL groups, HBGL and PBGL increased the immunoglobulin A (IgA) content at 13 wk of age and the IgM content at 7 wk of age (P < 0.05). The bone mineral density (BMD) at 7 and 13 wk of age and tibial strength (TS) at 13 wk of age of the pullets in the WL group were significantly higher than those in the HBGL and PBGL group (P < 0.05). Osteoclastogenesis inhibitory factor gene (OPG mRNA) expression was increased in the layer chickens at the age of 7 and 13 wk for the WL group (P < 0.05). Compared with the WL group and PBGL group, the melanopsin gene (OPN4 mRNA) transcription level of hypothalamus and pineal gland of the chickens under HBGL significantly increased at 7 and 13 wk of age (P < 0.05). In conclusion, blue-green LED light with two perceived illuminance (human and poultry) can increase the Ig content and the immune performance of layer chickens, and blue-green LED light (light intensity unit lux) can promote the expression of OPN4 gene in the hypothalamus and pineal gland. In addition, white LED light can enhance bone quality by increasing tibia OPG gene expression.
Keywords: blue-green LED light; bone development; immune performance; layer chickens; spectral sensitivity.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Effects of a two-phase mixed color lighting program using light-emitting diode lights on layer chickens during brooding and rearing periods.Poult Sci. 2020 Oct;99(10):4695-4703. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2020.06.072. Epub 2020 Jul 31. Poult Sci. 2020. PMID: 32988504 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of fluorescent vs. poultry-specific light-emitting diode lights on production performance and egg quality of W-36 laying hens.Poult Sci. 2018 Mar 1;97(3):834-844. doi: 10.3382/ps/pex371. Poult Sci. 2018. PMID: 29272505
-
Rearing system affects prevalence of keel-bone damage in laying hens: a longitudinal study of four consecutive flocks.Poult Sci. 2017 Jul 1;96(7):2029-2039. doi: 10.3382/ps/pex026. Poult Sci. 2017. PMID: 28371938
-
Effects of Key Farm Management Practices on Pullets Welfare-A Review.Animals (Basel). 2022 Mar 14;12(6):729. doi: 10.3390/ani12060729. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35327126 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of the immune system of chickens a key factor in maintaining poultry production-a review.Poult Sci. 2023 Aug;102(8):102785. doi: 10.1016/j.psj.2023.102785. Epub 2023 May 19. Poult Sci. 2023. PMID: 37267642 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Light-induced epigenetic modifications in the hypothalamus during avian embryonic development enhance phenotypic plasticity.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025 Jun 26;13:1573705. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2025.1573705. eCollection 2025. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2025. PMID: 40641602 Free PMC article.
-
Modulating effects of Phellinus linteus polysaccharides on antioxidant capacity, immune function, intestinal function and microbiota in lipopolysaccharide-challenged broilers.Front Microbiol. 2025 May 27;16:1570370. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1570370. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40497052 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of LED Lights with Defined Spectral Proportion on Growth and Reproduction of Indigenous Beijing-You Chickens.Animals (Basel). 2023 Feb 9;13(4):616. doi: 10.3390/ani13040616. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36830401 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Amoroso L., Baraldi A., Barreiro F., Pacheco M., Alva J., Soares N., Pacheco L., Melaré M. Bone densitometry and calcium serum levels in chickens treated with filtered or unfiltered water. Rev. Bras. Ciênc. Avíc. 2013;15:379–384.
-
- Bailey M.J., Cassone V.M. Melanopsin expression in the chick retina and pineal gland. Mol. Brain. Res. 2005;134:345–348. - PubMed
-
- Baxter M., Joseph N., Osborne V.R., Bédécarrats G.Y. Red light is necessary to activate the reproductive axis in chickens independently of the retina of the eye. Poult. Sci. 2014;93:1289–1297. - PubMed
-
- Bédécarrats G.Y. Control of the reproductive axis: Balancing act between stimulatory and inhibitory inputs. Poult. Sci. 2015;94:810–815. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

