Sepsis Management for the Nephrologist
- PMID: 35551069
- PMCID: PMC9269656
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.14381121
Sepsis Management for the Nephrologist
Abstract
The definition of sepsis has evolved significantly over the past three decades. Today, sepsis is defined as a dysregulated host immune response to microbial invasion leading to end organ dysfunction. Septic shock is characterized by hypotension requiring vasopressors after adequate fluid resuscitation with elevated lactate. Early recognition and intervention remain hallmarks for sepsis management. We addressed the current literature and assimilated thought regarding optimum initial resuscitation of the patient with sepsis. A nuanced understanding of the physiology of lactate is provided in our review. Physiologic and practical knowledge of steroid and vasopressor therapy for sepsis is crucial and addressed. As blood purification may interest the nephrologist treating sepsis, we have also added a brief discussion of its status.
Keywords: acute kidney injury; critical care nephrology and acute kidney injury series; sepsis; septic shock.
Copyright © 2022 by the American Society of Nephrology.
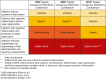
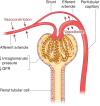
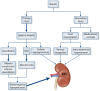
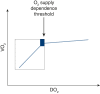
Figures

References
-
- Kaukonen KM, Bailey M, Suzuki S, Pilcher D, Bellomo R: Mortality related to severe sepsis and septic shock among critically ill patients in Australia and New Zealand, 2000-2012. JAMA 311: 1308–1316, 2014 - PubMed
-
- Martin GS, Mannino DM, Eaton S, Moss M: The epidemiology of sepsis in the United States from 1979 through 2000. N Engl J Med 348: 1546–1554, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Bagshaw SM, Lapinsky S, Dial S, Arabi Y, Dodek P, Wood G, Ellis P, Guzman J, Marshall J, Parrillo JE, Skrobik Y, Kumar A; Cooperative Antimicrobial Therapy of Septic Shock (CATSS) Database Research Group : Acute kidney injury in septic shock: Clinical outcomes and impact of duration of hypotension prior to initiation of antimicrobial therapy. Intensive Care Med 35: 871–881, 2009 - PubMed
-
- Evans L, Rhodes A, Alhazzani W, Antonelli M, Coopersmith CM, French C, Machado FR, Mcintyre L, Ostermann M, Prescott HC, Schorr C, Simpson S, Joost Wiersinga W, Alshamsi F, Angus DC, Arabi Y, Azevedo L, Beale R, Beilman G, Belley-Cote E, Burry L, Cecconi M, Centofanti J, Yataco AC, De Waele J, Dellinger RP, Doi K, Du B, Estenssoro E, Ferrer R, Gomersall C, Hodgson C, Møller MH, Iwashyna T, Jacob S, Kleinpell R, Klompas M, Koh Y, Kumar A, Kwizera A, Lobo S, Masur H, McGloughlin S, Mehta S, Mehta Y, Mer M, Nunnally M, Oczkowski S, Osborn T, Papathanassoglou E, Perner A, Puskarich M, Roberts J, Schweickert W, Seckel M, Sevransky J, Sprung CL, Welte T, Zimmerman J, Levy M: Executive summary: Surviving Sepsis Campaign: International guidelines for the management of sepsis and septic shock 2021. Crit Care Med 49: 1974–1982, 2021 - PubMed
-
- Bone RC, Balk RA, Cerra FB, Dellinger RP, Fein AM, Knaus WA, Schein RM, Sibbald WJ; The ACCP/SCCM Consensus Conference Committee. American College of Chest Physicians/Society of Critical Care Medicine : Definitions for sepsis and organ failure and guidelines for the use of innovative therapies in sepsis. Chest 101: 1644–1655, 1992 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

