Immunoglobulin repletion during blinatumomab therapy does not reduce the rate of secondary hypogammaglobulinemia and associated infectious risk
- PMID: 35551109
- PMCID: PMC9242831
- DOI: 10.5045/br.2022.2021163
Immunoglobulin repletion during blinatumomab therapy does not reduce the rate of secondary hypogammaglobulinemia and associated infectious risk
Abstract
Background: Blinatumomab has demonstrated efficacy in minimal residual disease (MRD) positive and relapsed/refractory B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) by inciting rapid and sustained B-cell depletion.
Methods: Owing to its effect on B-cells, blinatumomab is associated with a higher rate of secondary hypogammaglobulinemia compared to chemotherapy. To mitigate blinatumomab-induced hypogammaglobulinemia, patients were pre-emptively repleted with intravenous immune globulin (IVIG) during blinatumomab therapy. In this retrospective study, we compared outcomes of 23 blinatumomab treated adults with ALL. Seventeen patients routinely received IVIG and 6 patients were in the control cohort.
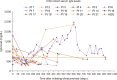
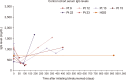
Results: Our findings demonstrated no difference between the two cohorts in immunoglobulin G (IgG) nadir (338 mg/dL vs. 337 mg/dL, P=0.641), days to IgG nadir (120.5 vs. 85.5 days, P=0.13), infection rate (82.4% vs. 66.7%, P=0.58), infections requiring ICU admission (23.5% vs. 16.7%, P=1), and infection related mortality (17.6% vs. 16.7%, P=1).
Conclusion: Pre-emptive IVIG repletion during blinatumomab did not prevent hypogammaglobulinemia and associated infection risk.
Keywords: ALL; Acute lymphoblastic leukemia; Blinatumomab; Hypogammaglobulinemia; Intravenous Immunoglobulin.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this article were reported.
Figures
References
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network, author. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia (version 2.2020) National Comprehensive Cancer Network; Plymouth Meeting, PA: 2020. [Accessed November 28, 2020]. at https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/pdf/all.pdf .
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources