Sleep onset, duration, or regularity: which matters most for child adiposity outcomes?
- PMID: 35551259
- PMCID: PMC9585919
- DOI: 10.1038/s41366-022-01140-0
Sleep onset, duration, or regularity: which matters most for child adiposity outcomes?
Abstract
Background/objectives: Sleep measures, such as duration and onset timing, are associated with adiposity outcomes among children. Recent research among adults has considered variability in sleep and wake onset times, with the Sleep Regularity Index (SRI) as a comprehensive metric to measure shifts in sleep and wake onset times between days. However, little research has examined regularity and adiposity outcomes among children. This study examined the associations of three sleep measures (i.e., sleep duration, sleep onset time, and SRI) with three measures of adiposity (i.e., body mass index [BMI], waist circumference, and waist-to-height ratio [WHtR]) in a pediatric sample.
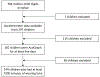
Subjects/methods: Children (ages 4-13 years) who were part of the U.S. Newborn Epigenetic STudy (NEST) participated. Children (N = 144) wore an ActiGraph for 1 week. Sleep measures were estimated from actigraphy data. Weight, height, and waist circumference were measured by trained researchers. BMI and WHtR was calculated with the objectively measured waist and height values. Multiple linear regression models examined associations between child sleep and adiposity outcomes, controlling for race/ethnicity, child sex, age, mothers' BMI and sleep duration.
Results: When considering sleep onset timing and duration, along with demographic covariates, sleep onset timing was not significantly associated with any of the three adiposity measures, but a longer duration was significantly associated with a lower BMI Z-score (β = -0.29, p < 0.001), waist circumference (β = -0.31, p < 0.001), and WHtR (β = -0.38, p < 0.001). When considering SRI and duration, duration remained significantly associated with the adiposity measures. The SRI and adiposity associations were in the expected direction, but were non-significant, except the SRI and WHtR association (β = -0.16, p = 0.077) was marginally non-significant.
Conclusions: Sleep duration was consistently associated with adiposity measures in children 4-13 years of age. Pediatric sleep interventions should focus first on elongating nighttime sleep duration, and examine if this improves child adiposity outcomes.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Miller MA, Bates S, Ji C, Cappuccio FP. Systematic review and meta-analyses of the relationship between short sleep and incidence of obesity and effectiveness of sleep interventions on weight gain in preschool children. Obes Rev. 2021;22(2):e13113. - PubMed
-
- Ash T, Taveras EM. Associations of short sleep duration with childhood obesity and weight gain: summary of a presentation to the National Academy of Science’s Roundtable on Obesity Solutions. Sleep Health. 2017. Oct;3(5):389–92. - PubMed
-
- Fatima Y, Doi S a. R, Mamun AA. Longitudinal impact of sleep on overweight and obesity in children and adolescents: a systematic review and bias-adjusted meta-analysis. Obes Rev. 2015;16(2):137–49. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources