Validated determination of NRG1 Ig-like domain structure by mass spectrometry coupled with computational modeling
- PMID: 35551273
- PMCID: PMC9098640
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-022-03411-y
Validated determination of NRG1 Ig-like domain structure by mass spectrometry coupled with computational modeling
Abstract
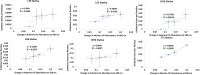
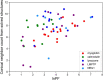
High resolution hydroxyl radical protein footprinting (HR-HRPF) is a mass spectrometry-based method that measures the solvent exposure of multiple amino acids in a single experiment, offering constraints for experimentally informed computational modeling. HR-HRPF-based modeling has previously been used to accurately model the structure of proteins of known structure, but the technique has never been used to determine the structure of a protein of unknown structure. Here, we present the use of HR-HRPF-based modeling to determine the structure of the Ig-like domain of NRG1, a protein with no close homolog of known structure. Independent determination of the protein structure by both HR-HRPF-based modeling and heteronuclear NMR was carried out, with results compared only after both processes were complete. The HR-HRPF-based model was highly similar to the lowest energy NMR model, with a backbone RMSD of 1.6 Å. To our knowledge, this is the first use of HR-HRPF-based modeling to determine a previously uncharacterized protein structure.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing interests: J.S.S. has a financial interest in GenNext Technologies, Inc., a company commercializing technologies for protein higher structure analysis.
Figures

References
-
- Yugandhar K., Zhao Q., Gupta S., Xiong D., Yu H. Progress in methodologies and quality-control strategies in protein cross-linking mass spectrometry. Proteomics21, e2100145 (2021). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

