BCR::ABL1 tyrosine kinase inhibitors hamper the therapeutic efficacy of blinatumomab in vitro
- PMID: 35551463
- PMCID: PMC9470724
- DOI: 10.1007/s00432-022-04039-5
BCR::ABL1 tyrosine kinase inhibitors hamper the therapeutic efficacy of blinatumomab in vitro
Abstract
Purpose: Acute B-lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL) is a malignant disease characterized by accumulation of clonal immature lymphocytes in the bone marrow and peripheral blood. The approval of BCR::ABL1 tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKI) such as imatinib, dasatinib, nilotinib and ponatinib marked a milestone in targeted therapy only for a subset of patients carrying the translocation t(9;22)(q34;q11). Immunotherapy with the bispecific antibody (bsAb) blinatumomab targeting CD19xCD3 revolutionized treatment of all B-ALL cases. The combination of both TKI and bsAb, so-called "dual targeting", is currently under clinical investigation, although TKI might influence T cell effects.
Methods: We here investigated the combination of different TKI and blinatumomab in BCR::ABL1+ and BCR::ABL1- B-ALL cell lines and primary samples regarding T cell proliferation, differentiation, cytokine release and killing of tumor cells.
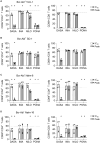
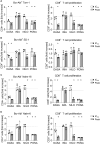
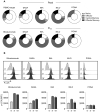
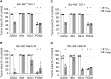
Results: In vitro analysis revealed profound reduction of T cell proliferation, differentiation, cytokine release and killing of tumor cells upon application of BCR::ABL1 TKI with blinatumomab. Inhibition was more pronounced with dasatinib and ponatinib compared to nilotinib and imatinib. T cell signalling after CD3 stimulation was impaired by TKI mirrored by inhibition of LCK phosphorylation. This known off-target effect might influence the efficacy of bsAb therapy when combined with BCR::ABL1 TKI.
Conclusion: In conclusion, we propose that nilotinib and imatinib might also be suitable substances for combination with blinatumomab and suggest evaluation in clinical trials.
Keywords: Acute lymphoblastic leukaemia; BCR::ABL1; Blinatumomab; Tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Assi R, Kantarjian H, Short NJ, Daver N, Takahashi K, Garcia-Manero G, DiNardo C, Burger J, Cortes J, Jain N (2017) Safety and efficacy of blinatumomab in combination with a tyrosine kinase inhibitor for the treatment of relapsed Philadelphia chromosome-positive leukemia. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk 17(12):897–901 - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

