No-nonsense: insights into the functional interplay of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay factors
- PMID: 35551602
- PMCID: PMC9162471
- DOI: 10.1042/BCJ20210556
No-nonsense: insights into the functional interplay of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay factors
Abstract
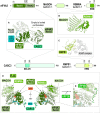
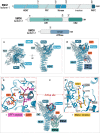
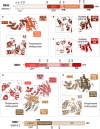
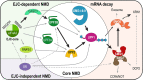
Nonsense-mediated messenger RNA decay (NMD) represents one of the main surveillance pathways used by eukaryotic cells to control the quality and abundance of mRNAs and to degrade viral RNA. NMD recognises mRNAs with a premature termination codon (PTC) and targets them to decay. Markers for a mRNA with a PTC, and thus NMD, are a long a 3'-untranslated region and the presence of an exon-junction complex (EJC) downstream of the stop codon. Here, we review our structural understanding of mammalian NMD factors and their functional interplay leading to a branched network of different interconnected but specialised mRNA decay pathways. We discuss recent insights into the potential impact of EJC composition on NMD pathway choice. We highlight the coexistence and function of different isoforms of up-frameshift protein 1 (UPF1) with an emphasis of their role at the endoplasmic reticulum and during stress, and the role of the paralogs UPF3B and UPF3A, underscoring that gene regulation by mammalian NMD is tightly controlled and context-dependent being conditional on developmental stage, tissue and cell types.
Keywords: exon-junction complexes; nonsense-mediated mRNA decay; regulation of gene expression; translational control; up-frameshift proteins.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The long and short of EJC-independent nonsense-mediated RNA decay.Biochem Soc Trans. 2023 Jun 28;51(3):1121-1129. doi: 10.1042/BST20221131. Biochem Soc Trans. 2023. PMID: 37145092 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of EJC-enhanced and EJC-independent NMD in human cells reveals two partially redundant degradation pathways.RNA. 2013 Oct;19(10):1432-48. doi: 10.1261/rna.038893.113. Epub 2013 Aug 20. RNA. 2013. PMID: 23962664 Free PMC article.
-
Nonsense in the testis: multiple roles for nonsense-mediated decay revealed in male reproduction.Biol Reprod. 2017 May 1;96(5):939-947. doi: 10.1093/biolre/iox033. Biol Reprod. 2017. PMID: 28444146 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of nucleotide composition in premature termination codon recognition.BMC Bioinformatics. 2016 Dec 7;17(1):519. doi: 10.1186/s12859-016-1384-z. BMC Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 27927164 Free PMC article.
-
Mammalian UPF3A and UPF3B can activate nonsense-mediated mRNA decay independently of their exon junction complex binding.EMBO J. 2022 May 16;41(10):e109202. doi: 10.15252/embj.2021109202. Epub 2022 Apr 22. EMBO J. 2022. PMID: 35451102 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
SARS-CoV-2 Selectively Induces the Expression of Unproductive Splicing Isoforms of Interferon, Class I MHC, and Splicing Machinery Genes.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 23;25(11):5671. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115671. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38891862 Free PMC article.
-
Functional impact of splicing variants in the elaboration of complex traits in cattle.Nat Commun. 2025 Apr 24;16(1):3893. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-58970-5. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40274775 Free PMC article.
-
RNA Surveillance Factor SMG5 Is Essential for Mouse Embryonic Stem Cell Differentiation.Biomolecules. 2024 Aug 17;14(8):1023. doi: 10.3390/biom14081023. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 39199410 Free PMC article.
-
Differential alternative splicing landscape identifies potentially functional RNA binding proteins in early embryonic development in mammals.iScience. 2024 Feb 2;27(3):109104. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.109104. eCollection 2024 Mar 15. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38433915 Free PMC article.
-
The long and short of EJC-independent nonsense-mediated RNA decay.Biochem Soc Trans. 2023 Jun 28;51(3):1121-1129. doi: 10.1042/BST20221131. Biochem Soc Trans. 2023. PMID: 37145092 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

