The effects of macronutrients composition on hormones and substrates during a meal tolerance test in drugnaive and sitagliptin-treated individuals with type 2 diabetes: a randomized crossover study
- PMID: 35551683
- PMCID: PMC9832851
- DOI: 10.20945/2359-3997000000478
The effects of macronutrients composition on hormones and substrates during a meal tolerance test in drugnaive and sitagliptin-treated individuals with type 2 diabetes: a randomized crossover study
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the effect of sitagliptin treatment in early type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and the impact of different macronutrient compositions on hormones and substrates during meal tolerance tests (MTT).
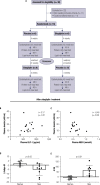
Methods: Half of the drug-naive patients with T2DM were randomly assigned for treatment with 100 mg of sitagliptin, q.d., or placebo for 4 weeks and then submitted to 3 consecutive MTT intercalated every 48 h. The MTTs differed in terms of macronutrient composition, with 70% of total energy from carbohydrates, proteins, or lipids. After 4 weeks of washout, a crossover treatment design was repeated. Both patients and researchers were blinded, and a repeated-measures ANOVA was employed for statistical analysis.
Results: Sitagliptin treatment reduced but did not normalize fasting and post-meal glucose values in the three MTTs, with lowered area-under-glucose-curve values varying from 7% to 15%. The sitagliptin treatment also improved the insulinogenic index (+86%) and the insulin/glucose (+25%), glucagon-like peptide-1/glucose (+46%) incremental area under the curves. Patients with early T2DM maintained the lowest glucose excursion after a protein- or lipid-rich meal without any major change in insulin, C-peptide, glucagon, or NEFA levels.
Conclusion: We conclude that sitagliptin treatment is tolerable and contributes to better control of glucose homeostasis in early T2DM, irrespective of macronutrient composition. The blood glucose excursion during meal ingestion is minimal in protein- or fat-rich meals, which can be a positive ally for the management of T2DM. Clinical trial no: NCT00881543.
Keywords: Diabetes; diet; glucose tolerance; glycemia; incretins; meal tolerance test.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: the CPO has been an employee of Eli Lilly and Company since 2010 and an owner of stock in Eli Lilly and Company. The remaining authors have no relevant conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Thornberry NA, Weber AE. Discovery of JANUVIA (Sitagliptin), a selective dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Curr Top Med Chem. 2007;7(6):557–568. - PubMed
-
- Miller S, St Onge EL. Sitagliptin: a dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Ann Pharmacother. 2006;40(7-8):1336–1343. - PubMed
-
- Williams-Herman D, Xu L, Teng R, Golm GT, Johnson J, Davies MJ, et al. Effect of initial combination therapy with sitagliptin and metformin on β-cell function in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012;14(1):67–76. - PubMed
-
- Lim S, An JH, Shin H, Khang AR, Lee Y, Ahn HY, et al. Factors predicting therapeutic efficacy of combination treatment with sitagliptin and metformin in type 2 diabetic patients: the COSMETIC study. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2012;77(2):215–223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
