Overview of Current Strategies Aiming at Improving Response to Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy
- PMID: 35552170
- PMCID: PMC9366342
- DOI: 10.5152/AnatolJCardiol.2022.1647
Overview of Current Strategies Aiming at Improving Response to Cardiac Resynchronization Therapy
Abstract
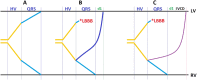
Cardiac resynchronization therapy is a treatment modality developed in the early 2000s that targets the mechanical and electrical dyssynchrony in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction patients. Appropriate patient selection conditions specified in the guidelines include measurement of left ventricular systolic dysfunction, QRS width, and assessment of functional classification. Despite consistent and increasing evidence sup-porting the use of cardiac resynchronization therapy in eligible patients, proportion of patients with the device is still not at the desired level. In addition, studies conducted in recent years have shown that the cardiac resynchronization therapy response of patients is quite heterogeneous and in echocardiographic follow-up, it was observed that reverse remodeling was not at the supposed level in approximately one-third of the patients. In order to change this result, which is due to many reasons, solutions such as using assistive imaging methods, providing optimal patient selection, trying different pacing techniques and post-procedural programming strategies (AV-delay and VV-delay optimization) have been the subject of debate. In this article, we aim to review the mechanisms that have been revealed regarding the differences in cardiac resynchronization therapy response and new pacing techniques-especially conduction system pacing-that may be preferred to resolve poor cardiac resynchronization therapy response.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

