Determination of trace elements in placenta by total reflection X-ray fluorescence spectrometry: effects of sampling and sample preparation
- PMID: 35552471
- PMCID: PMC9142463
- DOI: 10.1007/s00216-022-04112-5
Determination of trace elements in placenta by total reflection X-ray fluorescence spectrometry: effects of sampling and sample preparation
Abstract
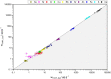
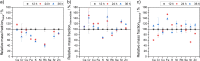
Placental elemental composition can serve as an indicator for neonatal health. Medical studies aiming at revealing such cause-and-effect relationships or studies monitoring potential environmental influences consist of large sample series to ensure statistically sufficient data. Several analytical techniques have been used to study trace metals in human placenta. However, most techniques require provision of clear liquid sample solutions and therefore time- and reagent-consuming total digestion of biological tissue is necessary. In total reflection X-ray fluorescence spectrometry (TXRF)-a straightforward multielement analytical technique-in contrast suspensions of minute sample amounts can be analyzed directly. Therefore, herein we report on a valid method to prepare homogenous sample suspensions for sustainable and fast TXRF analysis of large sample series. The optimized method requires only 10 mg of powdered placental tissue and 1 mL nitric acid. Suspensions are readily prepared within 30 min and the found mass fractions of major, minor, and trace elements are in good agreement in comparison to analysis of digests. In addition, possible effects on fixation time and the exact sampling location, i.e., maternal vs. fetal side of the placenta, were studied applying this method. Thereby, significant differences for fetal placenta tissue compared to maternal or intermediate tissue were observed revealing accumulation of trace elements in the fetal side of the placenta. Furthermore, considerable depletion of up to 60% mass fraction with longer fixation duration occurred in particular in fetal placenta tissue. These findings help to understand the large ranges of mass fraction of elements in placenta reported in the literature and at the same time indicate the necessity for more systematic investigation of non-homogenous elements distributed in placenta taking sampling and stabilization methods into account.
Keywords: Fetal and maternal tissue; Placenta; Sample preparation and stabilization; Suspension; TXRF; Trace elements.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Bioanalytical Application of the Total-Reflection X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometry.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 26;26(3):1049. doi: 10.3390/ijms26031049. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39940817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Total reflection X-ray spectrometry (TXRF) for trace elements assessment in edible clams.Appl Spectrosc. 2014;68(11):1241-6. doi: 10.1366/13-07364. Epub 2014 Oct 1. Appl Spectrosc. 2014. PMID: 25286343
-
Features of sample preparation techniques in the total-reflection X-ray fluorescence analysis of tea leaves.Food Chem. 2021 May 1;343:128502. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128502. Epub 2020 Oct 31. Food Chem. 2021. PMID: 33153812
-
Total reflection X-ray fluorescence spectrometry for trace determination of iron and some additional elements in biological samples.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2020 Sep;412(24):6419-6429. doi: 10.1007/s00216-020-02614-8. Epub 2020 Apr 26. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2020. PMID: 32337622 Free PMC article.
-
Recent trends in total reflection X-ray fluorescence spectrometry for biological applications.Anal Chim Acta. 2009 Feb 2;633(1):1-18. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2008.11.009. Epub 2008 Nov 14. Anal Chim Acta. 2009. PMID: 19110110 Review.
Cited by
-
Bioanalytical Application of the Total-Reflection X-Ray Fluorescence Spectrometry.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jan 26;26(3):1049. doi: 10.3390/ijms26031049. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39940817 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Placental Element Content Assessed via Synchrotron-Based X-ray Fluorescence Microscopy Identifies Low Molybdenum Concentrations in Foetal Growth Restriction, Postdate Delivery and Stillbirth.Nutrients. 2024 Aug 3;16(15):2549. doi: 10.3390/nu16152549. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39125428 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Iyengar GV, Rapp A. Human placenta as a ‘dual’ biomarker for monitoring fetal and maternal environment with special reference to potentially toxic trace elements. Part 3: Toxic trace elements in placenta and placenta as a biomarker for these elements. Sci Total Environ. 2001;280:221–238. doi: 10.1016/S0048-9697(01)00827-0. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Iyengar GV, Rapp A. Human placenta as a ‘dual’ biomarker for monitoring fetal and maternal environment with special reference to potentially toxic trace elements.: Part 2: Essential minor, trace and other (non-essential) elements in human placenta. Sci Total Environ. 2001;280:207–219. doi: 10.1016/S0048-9697(01)00826-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gómez-Roig M, Mazarico E, Cuadras D, Muniesa M, Pascal R, Ferrer P, Cantallops M, Arraez M, Gratacós E, Falcon M. Placental chemical elements concentration in small fetuses and its relationship with Doppler markers of placental function. Placenta. 2021;110:1–8. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2021.05.001. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

