Nanotechnology-Assisted Metered-Dose Inhalers (MDIs) for High-Performance Pulmonary Drug Delivery Applications
- PMID: 35552983
- PMCID: PMC9097569
- DOI: 10.1007/s11095-022-03286-y
Nanotechnology-Assisted Metered-Dose Inhalers (MDIs) for High-Performance Pulmonary Drug Delivery Applications
Erratum in
-
Correction: Nanotechnology-Assisted Metered-Dose Inhalers (MDIs) for High-Performance Pulmonary Drug Delivery Applications.Pharm Res. 2022 Nov;39(11):2857. doi: 10.1007/s11095-022-03306-x. Pharm Res. 2022. PMID: 35689006 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
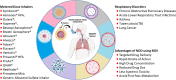
Purpose: Respiratory disorders pose a major threat to the morbidity and mortality to public health. Here we reviewed the nanotechnology based pulmonary drug delivery using metered dose inhalers.
Methods: Major respiratory diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases (COPD), asthma, acute lower respiratory tract infections, tuberculosis (TB) and lung cancer. At present, common treatments for respiratory disorders include surgery, radiation, immunotherapy, and chemotherapy or a combination. The major challenge is development of systemic delivery of the chemotherapeutic agents to the respiratory system. Conventional delivery of chemotherapy has various limitation and adverse side effected. Hence, targeted, and systemic delivery need to be developed. Towards this direction nanotechnology, based controlled, targeted, and systemic drug delivery systems are potential candidate to enhance therapeutic efficacy with minimum side effect. Among different route of administration, pulmonary delivery has unique benefits such as circumvents first pass hepatic metabolism and reduces dose and side effects.
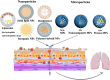
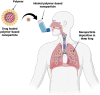
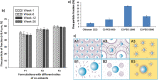
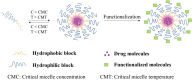
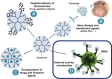
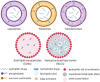
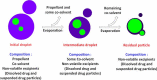
Results: Respiratory disorders pose a major threat to the morbidity and mortality to public health globally. Pulmonary delivery can be achieved through various drug delivery devices such as nebulizers, dry powder inhalers, and metered dose inhalers. Among them, metered dose inhalers are the most interesting and first choice of clinician over others. This review focused on nanotechnology based pulmonary drug delivery using metered dose inhalers. This report focused on delivery of various types of therapeutics using nanocarriers such as polymeric nanoparticles and micelles, dendrimers, lipid nanocarriers such as liposomes, solid lipid nanostructures and nanostructured lipid carriers, and other using metered dose inhalers discussed comprehensively. This report provides insight about the effect of parameters of MDI such as co-solvent, propellants, actuators shape, nozzle diameters, and jet lengths, and respiratory flow rate, and particle size of co-suspension of drug on aerodynamics and lung deposition of formulation. This review also provided the insight about various metered dose inhalers market scenario and digital metered dose inhalers.
Conclusion: This report concluded the clinical potential of metered dose inhalers, summary of current progress and future perspectives towards the smart digital metered dose inhalers development.
Keywords: cancer; drug delivery; metered dose inhalers; nanocarriers; pulmonary delivery.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature.
Figures

References
-
- Machhi J, Shahjin F, Das S, Patel M, Abdelmoaty MM, Cohen JD, Singh PA, Baldi A, Bajwa N, Kumar R, Vora LK, Patel TA, Oleynikov MD, Soni D, Yeapuri P, Mukadam I, Chakraborty R, Saksena CG, Herskovitz J, Hasan M, Oupicky D, Das S, Donnelly RF, Hettie KS, Chang L, Gendelman HE, Kevadiya BD. Nanocarrier vaccines for SARS-CoV-2. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2021;171:215–239. doi: 10.1016/J.ADDR.2021.01.002. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Machhi J, Shahjin F, Das S, Patel M, Abdelmoaty MM, Cohen JD, Singh PA, Baldi A, Bajwa N, Kumar R, Vora LK, Patel TA, Oleynikov MD, Soni D, Yeapuri P, Mukadam I, Chakraborty R, Saksena CG, Herskovitz J, Hasan M, Oupicky D, Das S, Donnelly RF, Hettie KS, Chang L, Gendelman HE, Kevadiya BD. A Role for Extracellular Vesicles in SARS-CoV-2 Therapeutics and Prevention. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2021;162(16):270–288. doi: 10.1007/S11481-020-09981-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Global Strategy for Asthma Management and Prevention (2016 update). (n.d.) www.ginasthma.org. Accessed 23 Feb 2022.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

