Addressing Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-gamma in 3-Nitropropionic Acid-Induced Striatal Neurotoxicity in Rats
- PMID: 35553009
- PMCID: PMC9167199
- DOI: 10.1007/s12035-022-02856-w
Addressing Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-gamma in 3-Nitropropionic Acid-Induced Striatal Neurotoxicity in Rats
Abstract
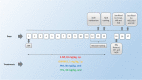
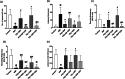
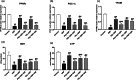
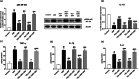
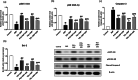
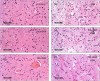
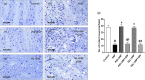
Telmisartan (TEL) is an angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker and a partial activator of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPARγ), which regulates inflammatory and apoptotic pathways. Increasing evidence has demonstrated the PPARγ agonistic property of TEL in several brain disorders. This study aims to explore the neuroprotective impact of TEL in 3-nitropropionic acid (3-NP)-induced neurotoxicity in rats. The PPARγ effect of TEL was affirmed by using the PPARγ agonist pioglitazone (PIO), and the antagonist GW9662. 3-NP led to a significant reduction in body weight alongside motor and cognitive functioning. The striata of the 3-NP-treated rats showed energy-deficit, microglia-mediated inflammatory reactions, apoptotic damage as well as histopathological lesions. PIO and TEL improved motor and cognitive perturbations induced by 3-NP, as confirmed by striatal histopathological examination, energy restoration, and neuronal preservation. Both drugs improved mitochondrial biogenesis evidenced by elevated mRNA expression of PPARγ, PGC-1α, and TFAM, alongside increased striatal ATP and SDH. The mitochondrial effect of TEL was beyond PPARγ activation. As well, their anti-inflammatory effect was attributed to suppression of microglial activation, and protein expression of pS536 p65 NF-κB with marked attenuation of striatal inflammatory mediator's release. Anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 expression was concurrently increased. TEL effectively participated in neuronal survival as it promoted phosphorylation of Akt/GSK-3β, further increased Bcl-2 expression, and inhibited cleavage of caspase-3. Interestingly, co-treatment with GW9662 partially revoked the beneficial effects of TEL. These findings recommend that TEL improves motor and cognitive performance, while reducing neuronal inflammation and apoptosis in 3-NP-induced neurotoxicity via a PPARγ-dependent mechanism.
Keywords: 3-nitropropionic acid; Neurotoxicity; Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ); Striatum.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Figures
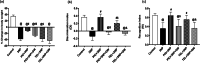
Similar articles
-
Telmisartan neuroprotective effects in 3-nitropropionic acid Huntington's disease model in rats: Cross talk between PPAR-γ and PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β pathway.Life Sci. 2022 May 15;297:120480. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.120480. Epub 2022 Mar 10. Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35278421
-
Telmisartan ameliorates Aβ oligomer-induced inflammation via PPARγ/PTEN pathway in BV2 microglial cells.Biochem Pharmacol. 2020 Jan;171:113674. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2019.113674. Epub 2019 Oct 18. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31634455
-
Telmisartan Protects a Microglia Cell Line from LPS Injury Beyond AT1 Receptor Blockade or PPARγ Activation.Mol Neurobiol. 2019 May;56(5):3193-3210. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1300-9. Epub 2018 Aug 13. Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30105672 Free PMC article.
-
Telmisartan protects central neurons against nutrient deprivation-induced apoptosis in vitro through activation of PPARγ and the Akt/GSK-3β pathway.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2014 Jun;35(6):727-37. doi: 10.1038/aps.2013.199. Epub 2014 May 5. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2014. PMID: 24793312 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Diabetic Effect of Telmisartan Through its Partial PPARγ-Agonistic Activity.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020 Oct 12;13:3627-3635. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S265399. eCollection 2020. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020. PMID: 33116714 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Amorfrutin B Compromises Hypoxia/Ischemia-induced Activation of Human Microglia in a PPARγ-dependent Manner: Effects on Inflammation, Proliferation Potential, and Mitochondrial Status.J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 1;19(1):34. doi: 10.1007/s11481-024-10135-9. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38949694 Free PMC article.
-
Direct Interaction of Minocycline to p47phox Contributes to its Attenuation of TNF-α-Mediated Neuronal PC12 Cell Death: Experimental and Simulation Validation.Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024 Jun;82(2):1261-1277. doi: 10.1007/s12013-024-01279-9. Epub 2024 May 13. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2024. PMID: 38739323
-
Cornerstone Cellular Pathways for Metabolic Disorders and Diabetes Mellitus: Non-Coding RNAs, Wnt Signaling, and AMPK.Cells. 2023 Nov 9;12(22):2595. doi: 10.3390/cells12222595. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37998330 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Metabolic Basis for Nervous System Dysfunction in Alzheimer's Disease, Parkinson's Disease, and Huntington's Disease.Curr Neurovasc Res. 2023;20(3):314-333. doi: 10.2174/1567202620666230721122957. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2023. PMID: 37488757 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular Metabolism: A Fundamental Component of Degeneration in the Nervous System.Biomolecules. 2023 May 11;13(5):816. doi: 10.3390/biom13050816. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37238686 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

