Personalised Medicine with IL-23 Blockers: Myth or Reality?
- PMID: 35553661
- PMCID: PMC9113162
- DOI: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjab190
Personalised Medicine with IL-23 Blockers: Myth or Reality?
Abstract
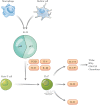
Background and aims: The medical management of inflammatory bowel disease [IBD] has become increasingly targeted, through the identification of specific immune mediators involved in its pathogenesis. IL-23 is an inflammatory cytokine involved in both innate and adaptive immunity, which has been identified as a therapeutic target in Crohn's disease [CD] and ulcerative colitis [UC] through its upstream inhibition of the T helper 17 [Th17] pathway. We sought to review available data on the efficacy of IL-23 inhibitors in the treatment of IBD and the potential for clinical and molecular predictors of response to facilitate a personalised medicine approach with these agents.
Methods: We reviewed and summarised available clinical trial data on the use of the IL-23 inhibitors risankizumab, brazikumab, mirikizumab, and guselkumab in the treatment of IBD, as well as the evidence from studies of these agents in IBD and other immune-mediated conditions which might inform prediction of response to IL-23 inhibition.
Results: Early clinical trials have demonstrated promising results following both induction and maintenance therapy with IL-23 inhibitors in CD and UC. Pre- and post-treatment levels of IL-22 and post-treatment levels of IL-17 have been identified as potential molecular predictors of response to therapy, in several studies. No significant clinical predictors of response have been identified thus far.
Conclusions: IL-23 antagonism is a promising therapeutic approach in IBD. Further exploration of molecular and clinical predictors of response may identify patients most likely to benefit from these medications.
Keywords: IBD; IL-23; p19.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation.
Figures
References
-
- Sands BE, Sandborn WJ, Panaccione R, et al. UNIFI Study Group. Ustekinumab as induction and maintenance therapy for ulcerative colitis. N Engl J Med 2019;381:1201–14. - PubMed
-
- Feagan BG, Sandborn WJ, Gasink C, et al. UNITI–IM-UNITI Study Group. Ustekinumab as induction and maintenance therapy for Crohn’s disease. N Engl J Med 2016;375:1946–60. - PubMed
-
- Moschen AR, Tilg H, Raine T. IL-12, IL-23 and IL-17 in IBD: immunobiology and therapeutic targeting. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2019;16:185–96. - PubMed

