IL-23 Monoclonal Antibodies for IBD: So Many, So Different?
- PMID: 35553664
- PMCID: PMC9097671
- DOI: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjac038
IL-23 Monoclonal Antibodies for IBD: So Many, So Different?
Abstract
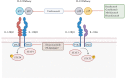
Interleukin [IL]-23 is a member of the IL-12 family of cytokines and has been implicated in multiple inflammatory disorders including psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and the inflammatory bowel diseases [IBDs]. Blockade of both IL-12 and IL-23 using an antibody that targets a shared subunit is highly effective in treating psoriasis, and recent data suggest similar efficacy in IBD with minimal adverse events. In this review, we summarise published data on the efficacy of anti-IL-12/23 therapies in IBD as well as emerging data on more selective anti-IL-23 specific therapies. Last, we discuss novel therapeutics under development which target the IL-23 pathway in unique ways and suggest that a biomarker-driven approach will soon guide clinicians to prescribe anti-IL-23 therapies to the patients most likely to respond to them.
Keywords: IL-23; Inflammatory bowel disease; monoclonal antibody.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation.
Figures
References
-
- Parham C, Chirica M, Timans J, et al. A receptor for the heterodimeric cytokine IL-23 is composed of IL-12Rbeta1 and a novel cytokine receptor subunit, IL-23R. J Immunol 2002;168:5699–708. - PubMed
-
- Thierfelder WE, van Deursen JM, Yamamoto K, et al. Requirement for Stat4 in interleukin-12-mediated responses of natural killer and T cells. Nature 1996;382:171–4. - PubMed
-
- Wilson NJ, Boniface K, Chan JR, et al. Development, cytokine profile and function of human interleukin 17-producing helper T cells. Nat Immunol 2007;8:950–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical