Blockade of IL-23: What is in the Pipeline?
- PMID: 35553666
- PMCID: PMC9097679
- DOI: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjab185
Blockade of IL-23: What is in the Pipeline?
Abstract
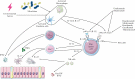
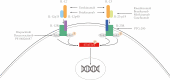
Interleukin 23 [IL-23] plays a key role in the pathogenesis of both Crohn's disease [CD] and ulcerative colitis [UC], promoting a Th17 cell-related immune response. The combined blockade of IL-23 and IL-12 with ustekinumab has been demonstrated to be safe and effective in the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease [IBD]. Studies on preclinical models and observations of other immune-mediated diseases, such as psoriasis, suggest that the selective inhibition of IL-23 could be beneficial in IBD. Four monoclonal antibodies [risankizumab, mirikizumab, brazikumab and guselkumab] are currently in advance clinical trials for either CD or UC. In this review, we provide an overview of the main results from published studies of selective anti IL-23 agents.
Keywords: Crohn’s disease; Interleukin 23; anti-IL23 monoclonal antibodies; interleukin 12; ulcerative colitis.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation.
Figures
References
-
- Macatonia SE, Hosken NA, Litton M, et al. Dendritic cells produce IL-12 and direct the development of Th1 cells from naive CD4+ T cells. J Immunol 1995;154:5071–9. - PubMed
-
- Szabo SJ, Kim ST, Costa GL, Zhang X, Fathman CG, Glimcher LH. A novel transcription factor, T-bet, directs Th1 lineage commitment. Cell 2000;100:655–69. - PubMed
-
- Moschen AR, Tilg H, Raine T. IL-12, IL-23 and IL-17 in IBD: immunobiology and therapeutic targeting. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 2019;16:185–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical