Ante-mortem plasma phosphorylated tau (181) predicts Alzheimer's disease neuropathology and regional tau at autopsy
- PMID: 35554506
- PMCID: PMC10233293
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awac175
Ante-mortem plasma phosphorylated tau (181) predicts Alzheimer's disease neuropathology and regional tau at autopsy
Abstract
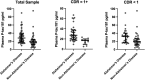
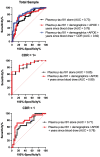
Blood-based biomarkers such as tau phosphorylated at threonine 181 (phosphorylated-tau181) represent an accessible, cost-effective and scalable approach for the in vivo detection of Alzheimer's disease pathophysiology. Plasma-pathological correlation studies are needed to validate plasma phosphorylated-tau181 as an accurate and reliable biomarker of Alzheimer's disease neuropathological changes. This plasma-to-autopsy correlation study included participants from the Boston University Alzheimer's Disease Research Center who had a plasma sample analysed for phosphorylated-tau181 between 2008 and 2018 and donated their brain for neuropathological examination. Plasma phosphorelated-tau181 was measured with single molecule array technology. Of 103 participants, 62 (60.2%) had autopsy-confirmed Alzheimer's disease. Average time between blood draw and death was 5.6 years (standard deviation = 3.1 years). Multivariable analyses showed higher plasma phosphorylated-tau181 concentrations were associated with increased odds for having autopsy-confirmed Alzheimer's disease [AUC = 0.82, OR = 1.07, 95% CI = 1.03-1.11, P < 0.01; phosphorylated-tau standardized (z-transformed): OR = 2.98, 95% CI = 1.50-5.93, P < 0.01]. Higher plasma phosphorylated-tau181 levels were associated with increased odds for having a higher Braak stage (OR = 1.06, 95% CI = 1.02-1.09, P < 0.01) and more severe phosphorylated-tau across six cortical and subcortical brain regions (ORs = 1.03-1.06, P < 0.05). The association between plasma phosphorylated-tau181 and Alzheimer's disease was strongest in those who were demented at time of blood draw (OR = 1.25, 95%CI = 1.02-1.53), but an effect existed among the non-demented (OR = 1.05, 95% CI = 1.01-1.10). There was higher discrimination accuracy for Alzheimer's disease when blood draw occurred in years closer to death; however, higher plasma phosphorylated-tau181 levels were associated with Alzheimer's disease even when blood draw occurred >5 years from death. Ante-mortem plasma phosphorylated-tau181 concentrations were associated with Alzheimer's disease neuropathology and accurately differentiated brain donors with and without autopsy-confirmed Alzheimer's disease. These findings support plasma phosphorylated-tau181 as a scalable biomarker for the detection of Alzheimer's disease.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; autopsy; biomarkers; plasma p-tau181; tau.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Guarantors of Brain. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Conflict of interest statement
K.J. has served as a consultant, at advisory boards, or at data monitoring committees for Abcam, Axon, BioArctic, Biogen, JOMDD/Shimadzu, Julius Clinical, Lilly, MagQu, Novartis, Pharmatrophix, Prothena, Roche Diagnostics and Siemens Healthineers, and is a co-founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB (BBS), which is a part of the GU Ventures Incubator Program, outside the work presented in this paper. H.K. has served at scientific advisory boards and/or as a consultant for Abbvie, Alector, Annexon, Artery Therapeutics, AZTherapies, CogRx, Denali, Eisai, Nervgen, Pinteon Therapeutics, Red Abbey Labs, Passage Bio, Roche, Samumed, Siemens Healthineers, Triplet Therapeutics and Wave; has given lectures in symposia sponsored by Cellectricon, Fujirebio, Alzecure, Biogen and Roche; and is a co-founder of Brain Biomarker Solutions in Gothenburg AB (BBS), which is a part of the GU Ventures Incubator Program. A.E.B. has served on consultant or advisory boards for Sage Pharmaceuticals and Cognito Therapeutics and has received grant monies from Biogen, Bristol Myers Squibb and Cyclerion. He receives publishing royalties from Elsevier and Oxford University Press. R.A. serves on the scientific advisory board of Signant Health, as consultant to Biogen and has given a lecture in a symposia sponsored by Eisai. R.A.S. has served as a consultant to Biogen and Lundbeck. He receives royalties for published neuropsychological tests from Psychological Assessment Resources, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Zetterberg H, Blennow K. Blood biomarkers: Democratizing Alzheimer’s diagnostics. Neuron. 2020;106:881–883. - PubMed
-
- Janelidze S, Mattsson N, Palmqvist S, et al. Plasma P-tau181 in Alzheimer’s disease: Relationship to other biomarkers, differential diagnosis, neuropathology and longitudinal progression to Alzheimer’s dementia. Nat Med. 2020;26:379–386. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- I01 CX001698/CX/CSRD VA/United States
- K23 NS102399/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U54 NS115266/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG068398/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R44 AG063635/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- IK2 CX002065/CX/CSRD VA/United States
- R01 AG066524/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- L30 NS093634/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001430/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG072978/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 681712/ERC_/European Research Council/International
- R56 AG062109/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- I01 CX001038/CX/CSRD VA/United States
- R01 NS017950/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AG068753/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

