DREAM interrupted: severing LIN-35-MuvB association in Caenorhabditis elegans impairs DREAM function but not its chromatin localization
- PMID: 35554539
- PMCID: PMC9252284
- DOI: 10.1093/genetics/iyac073
DREAM interrupted: severing LIN-35-MuvB association in Caenorhabditis elegans impairs DREAM function but not its chromatin localization
Abstract
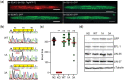
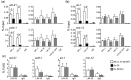
The mammalian pocket protein family, which includes the Retinoblastoma protein (pRb) and Rb-like pocket proteins p107 and p130, regulates entry into and exit from the cell cycle by repressing cell cycle gene expression. Although pRb plays a dominant role in mammalian systems, p107 and p130 are the ancestral pocket proteins. The Rb-like pocket proteins interact with the highly conserved 5-subunit MuvB complex and an E2F-DP transcription factor heterodimer, forming the DREAM (for Dp, Rb-like, E2F, and MuvB) complex. DREAM complex assembly on chromatin culminates in repression of target genes mediated by the MuvB subcomplex. Here, we examined how the Rb-like pocket protein contributes to DREAM formation and function by disrupting the interaction between the sole Caenorhabditis elegans pocket protein LIN-35 and the MuvB subunit LIN-52 using CRISPR/Cas9 targeted mutagenesis. A triple alanine substitution of LIN-52's LxCxE motif severed LIN-35-MuvB association and caused classical DREAM mutant phenotypes, including synthetic multiple vulvae, high-temperature arrest, and ectopic expression of germline genes in the soma. However, RNA-sequencing revealed limited upregulation of DREAM target genes when LIN-35-MuvB association was severed, as compared with gene upregulation following LIN-35 loss. Based on chromatin immunoprecipitation, disrupting LIN-35-MuvB association did not affect the chromatin localization of E2F-DP, LIN-35, or MuvB components. In a previous study, we showed that in worms lacking LIN-35, E2F-DP, and MuvB chromatin occupancy was reduced genome-wide. With LIN-35 present but unable to associate with MuvB, our study suggests that the E2F-DP-LIN-35 interaction promotes E2F-DP's chromatin localization, which we hypothesize supports MuvB chromatin occupancy indirectly through DNA. Altogether, this study highlights how the pocket protein's association with MuvB supports DREAM function but is not required for DREAM's chromatin occupancy.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9 genome editing; DREAM; MuvB; pocket protein; transcriptional repression.
© The Author(s) 2022. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Genetics Society of America. All rights reserved. For permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures




References
-
- Beitel GJ, Lambie EJ, Horvitz HR.. The C. elegans gene lin-9, which acts in an Rb-related pathway, is required for gonadal sheath cell development and encodes a novel protein. Gene. 2000;254(1–2):253–263. - PubMed
-
- Boichuk S, Parry JA, Makielski KR, Litovchick L, Baron JL, Zewe JP, Wozniak A, Mehalek KR, Korzeniewski N, Seneviratne DS, et al. The DREAM complex mediates GIST cell quiescence and is a novel therapeutic target to enhance imatinib-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2013;73(16):5120–5129. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

