Artifact reduction in contrast-enhanced mammography
- PMID: 35554734
- PMCID: PMC9098782
- DOI: 10.1186/s13244-022-01211-w
Artifact reduction in contrast-enhanced mammography
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the effectiveness of a new algorithm developed to reduce artifacts in dual-energy subtraction (DES) contrast-enhanced mammography (CEM) images while preserving contrast enhancement of possible lesions.
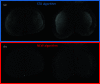
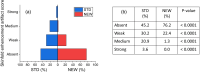
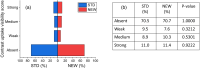
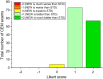
Methods: A retrospective multi-reader paired study was performed by using 134 CEM studies obtained from the first 134 women enrolled in a prospective clinical study aiming to compare the clinical performance of CEM to those of breast MRI in screening of women at increased risk of breast cancer. Four experienced readers compared independently the standard (STD) DES images with those obtained by reprocessing the raw images by a new algorithm (NEW), expected to reduce the DES artifact intensity. The intensity of three types of artifacts (breast-in-breast, ripple, and skinfold enhancement) and the intensity of possible contrast uptake were assessed visually and rated using a categorical ordinal scale. Proportions of images rated by the majority of readers as "Absent", "Weak", "Medium", "Strong" in each artifact intensity category were compared between the two algorithms. P-values lower than 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
Results: The NEW algorithm succeeded in eliminating 84.5% of breast-in-breast artifacts, 84.2% of ripple artifacts, and 56.9% of skinfold enhancement artifacts versus STD DES images, and reduced the artifact intensity in 12.1%, 13.0%, and 28.8% of the images, respectively. The visibility of lesion contrast uptake was the same with the STD and the NEW algorithms.
Conclusion: The new dual-energy subtraction algorithm demonstrated to be effective in reducing/eliminating CEM-related artifacts while preserving lesion contrast enhancement.
Keywords: Artifact; Contrast agent; Mammography.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures





References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

