Overexpression of BDNF in the ventrolateral periaqueductal gray regulates the behavior of epilepsy-migraine comorbid rats
- PMID: 35557046
- PMCID: PMC9226826
- DOI: 10.1002/brb3.2594
Overexpression of BDNF in the ventrolateral periaqueductal gray regulates the behavior of epilepsy-migraine comorbid rats
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) overexpression in the ventrolateral periaqueductal gray (vlPAG) on behavioral changes in epilepsy-migraine comorbid rats.
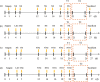
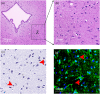
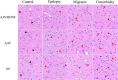
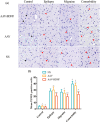
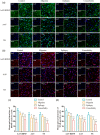
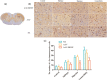
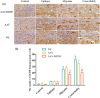
Method: We used an adeno-associated virus (AAV)-mediated vector to supplement BDNF in the vlPAG area prior to the establishment of a pilocarpine-nitroglycerin (Pilo-NTG) combination-induced comorbid model of epilepsy and migraine. Seizure- and migraine-related behaviors were analyzed. Cell loss and apoptosis in vlPAG were detected through hematoxylin-eosin (HE) and TUNEL staining. Immunofluorescence staining analyses were employed to detect expressions of BDNF and its receptor, tyrosine kinase B (TrkB), in vlPAG. Immunohistochemical staining was conducted to detect expressions of c-Fos and calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) in the trigeminal nucleus caudalis (TNC) and trigeminal ganglion (TG).
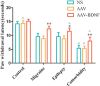
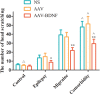
Results: Comparing to control group, AAV-BDNF injected comorbid group showed lower pain sensitivity, scratching head, and spontaneous seizures accompanied by the downregulation of c-Fos labeling neurons and CGRP immunoreactivity in the TNC and TG. However, these changes were still significantly higher in the comorbid group than those in both epilepsy and migraine groups under the same intervention.
Conclusion: These data demonstrated that supplying BDNF to vlPAG may protect structural and functional abnormalities in vlPAG and provide an antiepileptic and analgesic therapy.
Keywords: BDNF; comorbidity; epilepsy; migraine; ventrolateral periaqueductal gray.
© 2022 The Authors. Brain and Behavior published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Figures

References
-
- Akerman, S. , Holland, P. R. , & Goadsby, P. J. (2007). Cannabinoid (CB1) receptor activation inhibits trigeminovascular neurons. The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics, 320(1), 64–71. - PubMed
-
- Bartsch, T. , Knight, Y. E. , & Goadsby, P. J. (2004). Activation of 5‐HT(1B/1D) receptor in the periaqueductal gray inhibits nociception. Annals of Neurology, 56(3), 371–381. - PubMed
-
- Bovolenta, R. , Zucchini, S. , Paradiso, B. , Rodi, D. , Merigo, F. , Navarro Mora, G. , Osculati, F. , Berto, E. , Marconi, P. , Marzola, A. , Febene, P. A. , & Simonato, M. (2010). Hippocampal FGF‐2 and BDNF overexpression attenuates epileptogenesis‐associated neuroinflammation and reduces spontaneous recurrent seizures. Journal of Neuroinflammation, 7, 81. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Casarotto, P. C. , de Bortoli, V. C. , Correa, F. M. , Resstel, L. B. , & Zangrossi, H. Jr. (2010). Panicolytic‐like effect of BDNF in the rat dorsal periaqueductal grey matter: The role of 5‐HT and GABA. The International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology, 13(5), 573–582. - PubMed
-
- Chanda, M. L. , Tuttle, A. H. , Baran, I. , Atlin, C. , Guindi, D. , Hathaway, G. , Israelian, N. , Levenstadt, J. , Low, D. , Macrae, L. , O'Shea, L. , Silver, A. , Zendegui, E. , Lenselink, A. M. , Spijker, S. , Ferrari, M. D. , van den Maagdenberg, A. M. J. M. , & Mogil, J. S. (2013). Behavioral evidence for photophobia and stress‐related ipsilateral head pain in transgenic Cacna1a mutant mice. Pain, 154(8), 1254–1262. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

