A microarray expression profile and bioinformatic analysis of circular RNA in human esophageal carcinoma
- PMID: 35557573
- PMCID: PMC9086029
- DOI: 10.21037/jgo-22-137
A microarray expression profile and bioinformatic analysis of circular RNA in human esophageal carcinoma
Abstract
Background: Recent studies indicate that non-coding circular RNAs (circRNAs) are involved in the development of esophageal carcinoma (EC). This study aimed to identify differential expression of circRNAs in EC, which can provide potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets for EC treatment and improve the understanding of tumorigenesis mechanism.
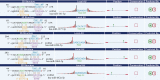
Methods: First, samples (n=5) of EC tissues and adjacent normal tissue were sent for circRNA microarray detection, Second, further bioinformatic analysis was performed, including circRNA-microRNA (miRNA), co-expression network analysis, Spearman correlation test, and cancer-related circRNA-miRNA axis analysis. Finally, the expression of circRNA that our analysis predicted to be hub genes was verified in samples (n=15) of EC tissues and adjacent normal tissue by real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR).
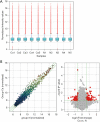
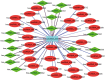
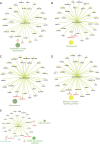
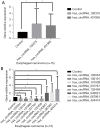
Results: Microarray identified 102 upregulated and 67 significantly downregulated circRNAs were in EC patients' tumors relative to adjacent normal tissue. One upregulated circRNA (hsa_circRNA_401955) showed the most connection with MREs, therefore was regarded as the hub gene by the Spearman correlation test. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway enrichment analyses showed that four primary pathways (mRNA surveillance, cytoskeleton actin regulation, spliceosome, and the NOD-like receptor signaling pathway) were predicted in the hub circRNA's five connected miRNA response elements (MREs). Furthermore, cancer-related circRNA-miRNA axis analyses showed that hsa_circRNA_100375 and its four connected MREs participated in the cancer-related pathway. RT-PCR showed that hsa_circRNA_100375 and hsa_circRNA_401955 were significantly increased in the tumor tissues of EC patients.
Conclusions: Abnormal expression of circRNAs was involved in the tumorigenesis of EC. Key circRNAs, namely hsa_circRNA_401955 and hsa_circRNA_100375, may be as potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets for the treatment of EC.
Keywords: Esophageal carcinoma (EC); bioinformatic analysis; circular RNAs (circRNAs); microRNA sponge; microarray.
2022 Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jgo.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jgo-22-137/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



References
-
- Hikami S, Shiozaki A, Fujiwara H, et al. Outcome of Patients with Pathological Complete Response after Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy in Advanced Esophageal Cancer. Gan To Kagaku Ryoho 2017;44:1796-8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
