Efficacy and safety of transarterial chemoembolization-lenvatinib sequential therapy for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: a retrospective study
- PMID: 35557575
- PMCID: PMC9086064
- DOI: 10.21037/jgo-22-239
Efficacy and safety of transarterial chemoembolization-lenvatinib sequential therapy for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: a retrospective study
Abstract
Background: The efficacy of transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with portal vein tumor thrombus (PVTT) is limited. There are insufficient data on TACE-lenvatinib sequential therapy for HCC with PVTT. We aimed to assess the efficacy and safety of TACE-lenvatinib sequential therapy for the treatment of HCC and PVTT.
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed 12 consecutive patients with HCC and PVTT who underwent TACE-lenvatinib sequential therapy between July 2018 and May 2021. Lenvatinib treatment was started 1 week after TACE at a dose of 8 or 12 mg daily depending on the patient weight. Follow-up examinations were performed at 4 week and then every 8 weeks after the first TACE procedure. Overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), objective response rate (ORR), disease control rate (DCR) and adverse events (AEs) were calculated. Survival curves of PFS and OS were estimated using the Kaplan-Meier method.
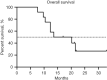
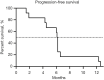
Results: The median OS and PFS were 16.9 and 6.15 months, respectively. The ORR and DCR were 75% and 91.7%, respectively. The most common lenvatinib-related AE was hypertension (33.3%), and the most common TACE-related AE was elevated liver enzymes (100%). No treatment-related deaths or grade 4 events were observed.
Conclusions: TACE-lenvatinib sequential therapy may be safe and well tolerated, and may improve OS and PFS for HCC patients with PVTT. Further randomized controlled trials with larger cohorts are needed to confirm its efficacy and safety.
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); lenvatinib; portal vein tumor thrombus (PVTT); sequential therapy; transarterial chemoembolization (TACE).
2022 Journal of Gastrointestinal Oncology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://jgo.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/jgo-22-239/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lenvatinib plus transarterial chemoembolization with or without immune checkpoint inhibitors for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A review.Front Oncol. 2022 Sep 28;12:980214. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.980214. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36249023 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transarterial chemoembolization plus lenvatinib versus transarterial chemoembolization plus sorafenib as first-line treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: A prospective randomized study.Cancer. 2021 Oct 15;127(20):3782-3793. doi: 10.1002/cncr.33677. Epub 2021 Jul 8. Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34237154 Clinical Trial.
-
Correlation and efficacy of TACE combined with lenvatinib plus PD-1 inhibitor in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus based on immunological features.Cancer Med. 2023 May;12(10):11315-11333. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5841. Epub 2023 Mar 23. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 36951443 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of transcatheter arterial chemoembolization-lenvatinib sequential therapy for patients with unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a single-arm clinical study.J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022 Jun;13(3):1367-1375. doi: 10.21037/jgo-22-525. J Gastrointest Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35837188 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative efficacy and safety of multimodality treatment for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus: patient-level network meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2024 Feb 16;14:1344798. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1344798. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38434681 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of hepatic arterial infusion chemotherapy in patients with primary liver cancer with portal vein tumor thrombosis: a comparative analysis of different perfusion chemotherapeutic regimens.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Sep 19;29(1):465. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-02053-6. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 39294739 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of clinical application of lenvatinib and its resistance mechanism in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (Review).Am J Cancer Res. 2024 Sep 15;14(9):4113-4171. doi: 10.62347/UJVP4361. eCollection 2024. Am J Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39417171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lenvatinib plus transarterial chemoembolization with or without immune checkpoint inhibitors for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: A review.Front Oncol. 2022 Sep 28;12:980214. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.980214. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36249023 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transarterial chemoembolization combined with sintilimab and lenvatinib for the treatment of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective study.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024 Sep 20;150(9):427. doi: 10.1007/s00432-024-05949-2. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39302490 Free PMC article.
-
The Combined Use of Lenvatinib and Locoregional Therapies for the Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2025 May 5;17(9):1572. doi: 10.3390/cancers17091572. Cancers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40361498 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Katamura Y, Aikata H, Takaki S, et al. Intra-arterial 5-fluorouracil/interferon combination therapy for advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with or without three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy for portal vein tumor thrombosis. J Gastroenterol 2009;44:492-502. 10.1007/s00535-009-0033-y - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous