Use of Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy With IR Biotyper® System for Legionella pneumophila Serogroups Identification
- PMID: 35558114
- PMCID: PMC9090449
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.866426
Use of Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy With IR Biotyper® System for Legionella pneumophila Serogroups Identification
Abstract
Legionella spp. are Gram-negative bacteria that inhabit freshwater environments representing a serious risk for human health. Legionella pneumophila (Lp) is the species most frequently responsible for a severe pneumonia known as Legionnaires' disease. Lp consists of 15 serogroups (Sgs), usually identified by monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies. With regard to Lp serogrouping, it is well known that phenotyping methods do not have a sufficiently high discriminating power, while genotypic methods although very effective, are expensive and laborious. Recently, mass spectrometry and infrared spectroscopy have proved to be rapid and successful approaches for the microbial identification and typing. Different biomolecules (e.g., lipopolysaccharides) adsorb infrared radiation originating from a specific microbial fingerprint. The development of a classification system based on the intra-species identification features allows a rapid and reliable typing of strains for diagnostic and epidemiological purposes. The aim of the study was the evaluation of Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy using the IR Biotyper® system (Bruker Daltonik, Germany) for the identification of Lp at the serogroup (Sg) level for diagnostic purposes as well as in outbreak events. A large dataset of Lp isolates (n = 133) and ATCC reference strains representing the 15 Lp serogroups were included. The discriminatory power of the instrument's classifier, was tested by Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA). All isolates were classified as follows: 12/133 (9.0%) as Lp Sg1 and 115/133 (86.5%) as Lp Sg 2-15 (including both ATCC and environmental Lp serogroup). Moreover, a mis-classification for 2/133 (1.5%) isolates of Lp Sg 2-15 that returned as Lp Sg1 was observed, and 4/133 (3.0%) isolates were not classified. An accuracy of 95.49% and an error rate of 4.51% were calculated. IR Biotyper® is able provide a quick and cost-effective reliable Lp classification with advantages compared with agglutination tests that show ambiguous and unspecific results. Further studies including a larger number of isolates could be useful to implement the classifier obtaining a robust and reliable tool for the routine Lp serogrouping. IR Biotyper® could be a powerful and easy-to-use tool to identify Lp Sgs, especially during cluster/outbreak investigations, to trace the source of the infection and promptly adopt preventive and control strategies.
Keywords: FTIR-spectroscopy; IR Biotyper®; Legionella pneumophila serogroups; diagnostics; environmental monitoring.
Copyright © 2022 Pascale, Bisognin, Mazzotta, Girolamini, Marino, Dal Monte, Cordovana, Scaturro, Ricci and Cristino.
Conflict of interest statement
MC was employed by Bruker Daltonic GmbH (the manufacturer of IR-Biotyper®). The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
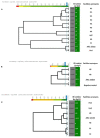
References
-
- Borges V., Nunes A., Sampaio D. A., Vieira L., Machado J., Simões M. J., et al. . (2016). Legionella pneumophila strain associated with the first evidence of person-to-person transmission of Legionnaireś disease: a unique mosaic genetic backbone. Sci. Rep. 6, 1–11. 10.1038/srep26261 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brunello A., Civilini M., De Martin S., Felice A., Franchi M., Iacumin L., et al. . (2022). Machine learning-assisted environmental surveillance of Legionella: a retrospective observational study in Friuli-Venezia Giulia region of Italy in the period 2002–2019. Inform Med. Unlocked 28, 100803. 10.1016/j.imu.2021.100803 - DOI
-
- Burckhardt I., Sebastian K., Mauder N., Kostrzewa M., Burckhardt F., Zimmermann S. (2019). Analysis of Streptococcus pneumoniae using Fourier-transformed infrared spectroscopy allows prediction of capsular serotype. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 38, 1883–1890. 10.1007/s10096-019-03622-y - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

