Immediate Lymphatic Reconstruction during Axillary Node Dissection for Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- PMID: 35558135
- PMCID: PMC9084431
- DOI: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000004291
Immediate Lymphatic Reconstruction during Axillary Node Dissection for Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Abstract
The objective of this study is to summarize the current body of evidence detailing the impact of immediate lymphatic reconstruction (ILR) on the incidence of breast cancer-related lymphedema (BCRL) following axillary node dissection (ALND).
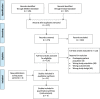
Methods: Medline and Embase databases were queried for publications, where ILR was performed at the time of ALND for breast cancer. Exclusion criteria included lymphaticovenous anastomosis for established BCRL, animal studies, non-breast cancer patient population studies, and descriptive studies detailing surgical technique. Meta-analysis was performed with a forest plot generated using a Mantel -Haenszel statistical method, with a random-effect analysis model. Effect measure was reported as risk ratios with associated 95% confidence intervals. The risk of bias within studies was assessed by the Cochrane Collaboration tool.
Results: This systematic review yielded data from 11 studies and 417 breast cancer patients who underwent ILR surgery at the time of ALND. There were 24 of 417 (5.7%) patients who developed BCRL following ILR. Meta-analysis revealed that in the ILR group, 6 of 90 patients (6.7%) developed lymphedema, whereas in the control group, 17 of 50 patients (34%) developed lymphedema. Patients in the ILR group had a risk ratio of 0.22 (CI, 0.09 -0.52) of lymphedema with a number needed to treat of four.
Conclusions: There is a clear signal indicating the benefit of ILR in preventing BCRL. Randomized control trials are underway to validate these findings. ILR may prove to be a beneficial intervention for improving the quality of life of breast cancer survivors.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of The American Society of Plastic Surgeons.
Figures
References
-
- Cook JA, Sasor SE, Loewenstein SN, et al. . Immediate lymphatic reconstruction after axillary lymphadenectomy: a single-institution early experience. Ann Surg Oncol. 2021;28:1381–1387. - PubMed
-
- Johnson AR, Kimball S, Epstein S, et al. . Lymphedema incidence after axillary lymph node dissection: quantifying the impact of radiation and the lymphatic microsurgical preventive healing approach. Ann Plast Surg. 2019;82(4S suppl 3):S234–S241. - PubMed
-
- Lucci A, McCall LM, Beitsch PD, et al. ; American College of Surgeons Oncology Group. Surgical complications associated with sentinel lymph node dissection (SLND) plus axillary lymph node dissection compared with SLND alone in the American College of Surgeons Oncology Group Trial Z0011. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25:3657–3663. - PubMed
-
- Khan F, Amatya B, Pallant JF, et al. . Factors associated with long-term functional outcomes and psychological sequelae in women after breast cancer. Breast. 2012;21:314–320. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources