Performance of an auto-adjusting prosthetic socket during walking with intermittent socket release
- PMID: 35558157
- PMCID: PMC9087223
- DOI: 10.1177/20556683221093271
Performance of an auto-adjusting prosthetic socket during walking with intermittent socket release
Abstract
Introduction: A challenge in the engineering of auto-adjusting prosthetic sockets is to maintain stable operation of the control system while users change their bodily position and activity. The purpose of this study was to test the stability of a socket that automatically adjusted socket size to maintain fit. Socket release during sitting was conducted between bouts of walking.
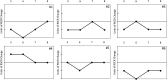
Methods: Adjustable sockets with sensors that monitored distance between the liner and socket were fabricated. Motor-driven panels and a microprocessor-based control system adjusted socket size during walking to maintain a target sensed distance. Limb fluid volume was recorded continuously. During eight sit/walk cycles, the socket panels were released upon sitting and then returned to position for walking, either the size at the end of the prior bout or a size 1.0% larger in volume.
Results: In six transtibial prosthesis users, the control system maintained stable operation and did not saturate (move to and remain at the end of the actuator's range) during 98% of the walking bouts. Limb fluid volume changes generally matched the panel position changes executed by the control system.
Conclusions: Stable operation of the control system suggests that the auto-adjusting socket is ready for testing in users' at-home settings.
Keywords: adjustable socket; amputee; control system; interface stress; pistoning; pressure; prosthesis; prosthetic; residual limb; socket fit; socket release; trans-tibial; volume accommodation.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures








References
-
- Legro MW, Reiber G, del Aguila M, et al. Issues of importance reported by persons with lower limb amputations and prostheses. J Rehabil Res Dev 1999; 36(3): 155–163. - PubMed
-
- Greenwald RM, Dean RC, Board WJ. Volume management: smart variable geometry socket (SVGS) technology for lower limb prostheses. J Prosthet Orthot 2003; 15(3): 107–112.
-
- Montgomery JT, Vaughan MR, Crawford RH. Design of an actively actuated prosthetic socket. Rapid Prototyp J 2010; 16(3): 194–201.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

