Agricultural wastes from wheat, barley, flax and grape for the efficient removal of Cd from contaminated water
- PMID: 35558207
- PMCID: PMC9091462
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra07877g
Agricultural wastes from wheat, barley, flax and grape for the efficient removal of Cd from contaminated water
Abstract
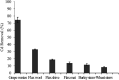
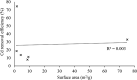
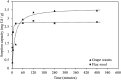
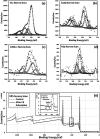
Agricultural production results in wastes that can be re-used to improve the quality of the environment. This work has investigated for the first time the use of abundant, un-modified agricultural wastes and by-products (AWBs) from grape, wheat, barley and flax production, to reduce the concentration of Cd, a highly toxic and mobile heavy metal, in contaminated water. At concentrations of 1.1 mg Cd per L, flax and grape waste were found superior in removing Cd compared with a granular activated carbon used in water treatment, which is both more expensive and entails greater CO2 emissions in its production. At a pH representative of mine effluents, where Cd presents its greatest mobility and risk as a pollutant, grape and flax waste showed capacity for effective bulk water treatment due to rapid removal kinetics and moderate adsorption properties: reaching equilibrium within 183 and 8 min - adsorption capacities were determined as 3.99 and 3.36 mg Cd per g, respectively. The capacity to clean contaminated effluents was not correlated with the surface area of the biosorbents. Surface chemistry analysis indicated that Cd removal is associated with exchange with Ca, and chemisorption involving CdCO3, CdS and CdO groups. This work indicates that some AWBs can be directly (i.e. without pre-treatment or modification) used in bulk to remediate effluents contaminated with heavy metals, without requiring further cost or energy input, making them potentially suitable for low-cost treatment of persistent (e.g. via mine drainage) or acute (e.g. spillages) discharges in rural and other areas.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Applicability of agricultural waste and by-products for adsorptive removal of heavy metals from wastewater.Bioresour Technol. 2013 Nov;148:574-85. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2013.08.124. Epub 2013 Aug 28. Bioresour Technol. 2013. PMID: 24045220 Review.
-
Microorganism and Agricultural Based Biosorbents Towards Removal of Cadmium from Waste-Water: An Overview.Recent Pat Biotechnol. 2017;11(3):204-217. doi: 10.2174/1872208311666170220121535. Recent Pat Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28219320 Review.
-
Mechanisms for the removal of Cd(II) and Cu(II) from aqueous solution and mine water by biochars derived from agricultural wastes.Chemosphere. 2020 Sep;254:126745. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.126745. Epub 2020 Apr 12. Chemosphere. 2020. PMID: 32315813
-
A critical review on the separation of heavy metal(loid)s from the contaminated water using various agricultural wastes.Int J Phytoremediation. 2024 Feb;26(3):349-368. doi: 10.1080/15226514.2023.2242973. Epub 2023 Aug 9. Int J Phytoremediation. 2024. PMID: 37559458 Review.
-
An extensive review on chromium (vi) removal using natural and agricultural wastes materials as alternative biosorbents.J Environ Health Sci Eng. 2021 Mar 10;19(1):1193-1207. doi: 10.1007/s40201-021-00641-w. eCollection 2021 Jun. J Environ Health Sci Eng. 2021. PMID: 34150305 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Biogenic nano-silver doped grapefruit peels biocomposite for biosorptive photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants.Sci Rep. 2025 May 19;15(1):17324. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-01318-2. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40389474 Free PMC article.
-
Multi-Analytical Approach for the Acid-Base, Thermal and Surface Properties Assessment of Waste Biomasses.Molecules. 2024 Dec 5;29(23):5735. doi: 10.3390/molecules29235735. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39683892 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative Biosorbents Based on Grape Pomace: Reducing Heavy Metals and Pesticides.Toxics. 2025 May 17;13(5):408. doi: 10.3390/toxics13050408. Toxics. 2025. PMID: 40423487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biosorbents from Plant Fibers of Hemp and Flax for Metal Removal: Comparison of Their Biosorption Properties.Molecules. 2021 Jul 10;26(14):4199. doi: 10.3390/molecules26144199. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34299474 Free PMC article.
-
Flax fiber based semicarbazide biosorbent for removal of Cr(VI) and Alizarin Red S dye from wastewater.Sci Rep. 2023 May 22;13(1):8267. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-34523-y. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37217542 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

