Protective effects of SKLB023 on a mouse model of unilateral ureteral obstruction by the modulation of gut microbiota
- PMID: 35558229
- PMCID: PMC9091184
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra08049f
Protective effects of SKLB023 on a mouse model of unilateral ureteral obstruction by the modulation of gut microbiota
Abstract
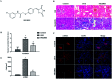
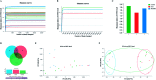
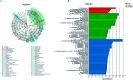
Renal interstitial fibrosis is the common pathway underlying the progression of chronic kidney disease (CKD) to end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and the corresponding therapies are limited. Quantitative and qualitative alterations in gut microbiota are noted in patients with CKD and ESRD. In our previous study, SKLB023 exhibited antifibrotic effects by interfering TGF-β1/Smad3 signaling in obstructive nephropathy. However, it remained unclear that oral administration of SKLB023 drives the alteration of gut microbiota to attenuate renal fibrosis. In the study, the marked inflammation and interstitial fibrosis were found in the kidney tissues of unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO) mice. While treatment with SKLB023 significantly alleviated renal interstitial fibrosis and reduced serum proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-6 levels. Importantly, SKLB023 derived the modulation of gut microbiota with the increasing similarity between the composition of gut microbiota in the control and UUO. The number of Turicibacter and Candidatus_Arthromitus was significantly decreased following UUO surgery and recovered by SKLB023, which positively correlated with pro-inflammatory cytokine expression. These results indicated the potential relationship between the antifibrotic benefits of SKLB023 and gut microbiota alteration, which provided new insights into drug therapy via gut microbiota modulation in obstructive nephropathy.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare. All authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
SKLB023 hinders renal interstitial fibrosis in obstructive nephropathy by interfering TGF-β1/Smad3 signaling.RSC Adv. 2018 Feb 6;8(11):5891-5896. doi: 10.1039/c8ra00018b. eCollection 2018 Feb 2. RSC Adv. 2018. PMID: 35539579 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-renal fibrosis effect of asperulosidic acid via TGF-β1/smad2/smad3 and NF-κB signaling pathways in a rat model of unilateral ureteral obstruction.Phytomedicine. 2019 Feb;53:274-285. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2018.09.009. Epub 2018 Sep 5. Phytomedicine. 2019. PMID: 30668407
-
Nootkatone confers antifibrotic effect by regulating the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway in mouse model of unilateral ureteral obstruction.Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 5;910:174479. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174479. Epub 2021 Sep 2. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34480883
-
Longitudinal analysis of fecal microbiome and metabolome during renal fibrotic progression in a unilateral ureteral obstruction animal model.Eur J Pharmacol. 2020 Nov 5;886:173555. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173555. Epub 2020 Sep 14. Eur J Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32937112
-
Gut Microbiota and Intestinal Epithelial Myd88 Signaling Are Crucial for Renal Injury in UUO Mice.Front Immunol. 2020 Dec 22;11:578623. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.578623. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 33414781 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Solt I. Kim M. J. Offer C. Harefuah. 2011;150:484–488. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

