The predictive performance of the lactate clearance rate combined with the APACHE II score in the prediction of sepsis-associated acute kidney injury in 7 days
- PMID: 35558275
- PMCID: PMC9085935
- DOI: 10.21037/tau-22-225
The predictive performance of the lactate clearance rate combined with the APACHE II score in the prediction of sepsis-associated acute kidney injury in 7 days
Abstract
Background: The purpose of this study was to evaluate the accuracy of the lactate clearance rate (LCR) combined with the Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II (APACHE II) score in the prediction of sepsis-associated acute kidney injury (SAKI).
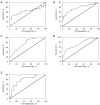
Methods: Sepsis patients were divided into the SAKI group and non-SAKI group. Arterial blood lactate was collected at 0 h (before treatment), 2 h, 4 h, 6 h, and 8 h (after treatment), and the LCR was calculated. The physiological parameters and laboratory test results were used to calculate the APACHE II score and the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves of LCR, APACHE II score and SOFA score for predicting patients with SAKI were drawn. Two single indicators with high areas under the curves (AUCs) were selected to calculate the joint probability through regression analysis, and the prediction efficiency corresponding to each curve was analyzed.
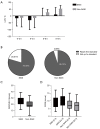
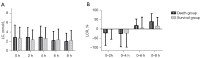
Results: There were significant differences in LCR between different groups and time periods (Fgroup=17.44, Pgroup ≤0.0001, Ftime =11.71, Ptime =0.0014). After 8 h of treatment, there was a significant difference in the overall compliance rate between the 2 groups (P<0.0001). In addition, after 24 h of treatment, the APACHE II score in the SAKI group was significantly higher than that in the non-SAKI group (P=0.0007), and SOFA score was also significantly higher than that in the non-SAKI group (P=0.0001). ROC curve showed that the 0-8 h LCR and APACHE II scores had a high predictive performance for the acute kidney injury (AKI) occurrence in sepsis patients, and AUCs were 0.7637 and 0.7517, respectively, while the combined AUC of the 2 indicators was 0.7975.
Conclusions: The 0-8 h LCR combined with APACHE II score can improve the early predictive value of SAKI, reduce the risk of AKI in patients with sepsis/septic shock, and reduce the social and family burden, which is worthy of clinical application.
Keywords: Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II (APACHE II) score; Lactate clearance rate (LCR); sepsis-associated acute kidney injury (SAKI).
2022 Translational Andrology and Urology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form (available at https://tau.amegroups.com/article/view/10.21037/tau-22-225/coif). The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Lactic acid, lactate clearance and procalcitonin in assessing the severity and predicting prognosis in sepsis].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020 Apr;32(4):449-453. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20200129-00086. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020. PMID: 32527351 Chinese.
-
[Combined prognostic value of serum lactic acid, procalcitonin and severity score for short-term prognosis of septic shock patients].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021 Mar;33(3):281-285. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20201113-00715. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2021. PMID: 33834968 Chinese.
-
[Predictive value of SOFA, qSOFA score and traditional evaluation index on sepsis prognosis].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2017 Aug;29(8):700-704. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2017.08.006. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2017. PMID: 28795667 Chinese.
-
Immunoregulatory mechanism of acute kidney injury in sepsis: A Narrative Review.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Mar;159:114202. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.114202. Epub 2023 Jan 6. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 36621143 Review.
-
The Response of Macrophages in Sepsis-Induced Acute Kidney Injury.J Clin Med. 2023 Jan 31;12(3):1101. doi: 10.3390/jcm12031101. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36769749 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development and validation of a model for predicting in-hospital mortality in patients with sepsis-associated kidney injury receiving renal replacement therapy: a retrospective cohort study based on the MIMIC-IV database.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Nov 4;14:1488505. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1488505. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39559702 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic values of noradrenaline administered dose, procalcitonin (PCT) and blood lactic acid for septic shock.J Med Biochem. 2025 Mar 21;44(2):319-329. doi: 10.5937/jomb0-53853. J Med Biochem. 2025. PMID: 40386512 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between Plasma Levels of Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein-1 (MCP-1) and 28-Day Mortality in Elderly Patients with Sepsis: A Retrospective Single-Center Study.Med Sci Monit. 2024 Jan 3;30:e942079. doi: 10.12659/MSM.942079. Med Sci Monit. 2024. PMID: 38169464 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of peripheral blood indicators plus procalcitonin clearance rate for mortality in cancer patients with sepsis.Am J Cancer Res. 2024 Dec 15;14(12):5839-5850. doi: 10.62347/NKOL2327. eCollection 2024. Am J Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39803656 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
