A lipopeptide biosurfactant from Bacillus sp. Lv13 and their combined effects on biodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene
- PMID: 35558302
- PMCID: PMC9090607
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra06693k
A lipopeptide biosurfactant from Bacillus sp. Lv13 and their combined effects on biodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene
Abstract
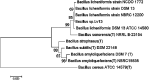
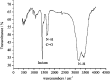
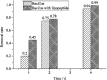
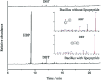
The process of using biodesulfurization (BDS) to remove sulfur compounds in petroleum has limitations such as low efficiency and low mass transfer. Therefore, it is important to study the combined effects of biosurfactant and the strain on BDS. A thermophilic desulfurization strain, Bacillus sp. Lv13, was isolated from the oilfield and used to produce biosurfactant (BS). The strain was identified as Bacillus licheniformis, a moderate thermophilic bacterium. Its BS was identified as lipopeptide using thin-layer chromatography (TLC), gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR). The emulsification efficiency after 24 h (E 24) and critical micelle concentration (CMC) were determined to be 46.93% and 30 mg L-1, respectively. The combined effects of biosurfactant and the strain on BDS was confirmed using the Gibbs assay, GC-MS and BaCl2 test. Results showed that the yield of 2-hydroxybiphenyl (2-HBP) from dibenzothiophene significantly increased after the addition of lipopeptide into the reaction system. This could be illustrated by the stabilization of emulsion, lower CMC value, higher mass transfer rate with the addition of lipopeptide, and the enhancement in the capacity of BDS as well as the catalytic ability of the microbial cell.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Stimulation of Bacillus sp. by lipopeptide biosurfactant for the degradation of aromatic amine 4-Chloroaniline.J Hazard Mater. 2021 Aug 5;415:125716. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.125716. Epub 2021 Mar 23. J Hazard Mater. 2021. PMID: 34088195
-
Purification and characterization of biosurfactant produced by Bacillus licheniformis Y-1 and its application in remediation of petroleum contaminated soil.Mar Pollut Bull. 2016 Jun 15;107(1):46-51. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.04.025. Epub 2016 Apr 22. Mar Pollut Bull. 2016. PMID: 27114088
-
Thermophilic desulfurization of dibenzothiophene and different petroleum oils by Klebsiella sp. 13T.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2012 Sep;19(8):3491-7. doi: 10.1007/s11356-012-0884-2. Epub 2012 Mar 31. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2012. PMID: 22467237
-
Thermophilic biodesulfurization and its application in oil desulfurization.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018 Nov;102(21):9089-9103. doi: 10.1007/s00253-018-9342-5. Epub 2018 Sep 10. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 30203145 Review.
-
Microbial desulfurization of organic sulfur compounds in petroleum.Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 1999 Jan;63(1):1-9. doi: 10.1271/bbb.63.1. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 1999. PMID: 10052116 Review.
Cited by
-
Microbial Surfactants: The Next Generation Multifunctional Biomolecules for Applications in the Petroleum Industry and Its Associated Environmental Remediation.Microorganisms. 2019 Nov 19;7(11):581. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms7110581. Microorganisms. 2019. PMID: 31752381 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterization of biosurfactant produced in response to petroleum crude oil stress by Bacillus sp. WD22 in marine environment.Braz J Microbiol. 2022 Dec;53(4):2015-2025. doi: 10.1007/s42770-022-00811-4. Epub 2022 Sep 2. Braz J Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 36053434 Free PMC article.
-
Isolation and Identification of Burkholderia stagnalis YJ-2 from the Rhizosphere Soil of Woodsia ilvensis to Explore Its Potential as a Biocontrol Agent Against Plant Fungal Diseases.Microorganisms. 2025 May 31;13(6):1289. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms13061289. Microorganisms. 2025. PMID: 40572177 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

