Investigating the Association Between rs2439302 Polymorphism and Thyroid Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 35558387
- PMCID: PMC9086625
- DOI: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.877206
Investigating the Association Between rs2439302 Polymorphism and Thyroid Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background and aims: The extent of surgical treatment for most patients with thyroid cancer (TC) remains controversial and varies widely. As an emerging technology, genetic testing facilitates tumor typing and disease progression monitoring and is expected to influence the choice of surgical approach for patients with TC. Recent genome-wide association studies (GWASs) have identified that rs2439302 (8p12) variants near NRG1 are associated with TC risk; however, the results remain inconclusive. Therefore, we aimed to perform a meta-analysis to clarify the association between rs2439302 variants and the risk of TC.
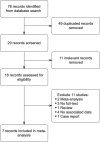
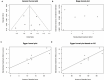
Methods: We search eligible studies using Pubmed, Scopus, Embase, Web of Science, and Cochrane library by July 2021. We analyzed the pooled OR and the corresponding 95% confidence interval (95% CI) of the included studies and then conducted subgroup analysis according to the ethnicity. We also performed a sensitivity analysis to validate the findings.
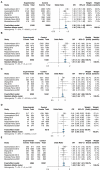
Results: This meta-analysis finally included 7 studies involving 6,090 cases and 14,461 controls. Results showed that the G allele of the rs2439302 polymorphism was a significant risk factor of TC in Allele (G/C), Dominant (GG+GC/CC), Recessive (GG/GC+CC), Homozygote (GG/CC), Heterozygote (GC/CC) models, with pooled ORs of 1.38 (95%CI, 1.31-1.45), 1.51 (95%CI, 1.41-1.62), 1.52 (95%CI, 1.40-1.66), 1.90 (95%CI, 1.71-2.10), and 1.40 (95%CI, 1.30-1.51), respectively. The subgroup analysis showed that rs2439302 polymorphism was associated with higher TC risk in different ethnicities with OR > 1. The sensitivity analysis exhibited that the results were stable by omitting any included studies.
Conclusions: The study revealed that rs2439302 variants were associated with higher TC risk and may have a major influence on the choice of operative approach for patients with TC.
Keywords: genome-wide association studies; meta-analysis; rs2439302; single nucleotide polymorphism; thyroid cancer.
Copyright © 2022 Guo, Zhang, He, Zheng, Liu, Ge and Xu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Apolipoprotein A5 gene promoter region-1131T/C polymorphism is associated with risk of ischemic stroke and elevated triglyceride levels: a meta-analysis.Cerebrovasc Dis. 2012;33(6):558-65. doi: 10.1159/000338781. Epub 2012 Jun 8. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2012. PMID: 22688093
-
Association of a LSP1 gene rs3817198T>C polymorphism with breast cancer risk: evidence from 33,920 cases and 35,671 controls.Mol Biol Rep. 2011 Oct;38(7):4687-95. doi: 10.1007/s11033-010-0603-3. Epub 2010 Dec 2. Mol Biol Rep. 2011. PMID: 21127985
-
Genetic Association of XRCC1 Gene rs1799782, rs25487 and rs25489 Polymorphisms with Risk of Thyroid Cancer: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2017 Jan 1;18(1):263-270. doi: 10.22034/APJCP.2017.18.1.263. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2017. PMID: 28240845 Free PMC article.
-
The roles of ADIPOQ rs266729 and MTNR1B rs10830963 polymorphisms in patients with gestational diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis.Gene. 2020 Mar 10;730:144302. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.144302. Epub 2019 Dec 26. Gene. 2020. PMID: 31884106 Review.
-
Association of miR-146a rs2910164 polymorphism with squamous cell carcinoma risk: a meta-analysis.J BUON. 2015 May-Jun;20(3):829-41. J BUON. 2015. PMID: 26214637 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of common genetic risk factors for differentiated thyroid cancer in the Thai population.Biomed Rep. 2025 Jul 25;23(4):157. doi: 10.3892/br.2025.2035. eCollection 2025 Oct. Biomed Rep. 2025. PMID: 40777629 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Genetic Polymorphisms in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: A 2023 Update.Biomedicines. 2023 Apr 2;11(4):1075. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11041075. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37189693 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The interplay of common genetic variants NRG1 rs2439302 and RET rs2435357 increases the risk of developing Hirschsprung's disease.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Jul 7;11:1184799. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1184799. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 37484916 Free PMC article.
-
Drug repositioning in thyroid cancer: from point mutations to gene fusions.Front Oncol. 2024 May 8;14:1407511. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1407511. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38779099 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

