Image Quality Control in Lumbar Spine Radiography Using Enhanced U-Net Neural Networks
- PMID: 35558524
- PMCID: PMC9087032
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.891766
Image Quality Control in Lumbar Spine Radiography Using Enhanced U-Net Neural Networks
Abstract
Purpose: To standardize the radiography imaging procedure, an image quality control framework using the deep learning technique was developed to segment and evaluate lumbar spine x-ray images according to a defined quality control standard.
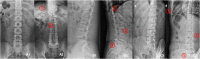
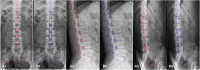
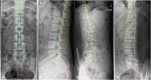
Materials and methods: A dataset comprising anteroposterior, lateral, and oblique position lumbar spine x-ray images from 1,389 patients was analyzed in this study. The training set consisted of digital radiography images of 1,070 patients (800, 798, and 623 images of the anteroposterior, lateral, and oblique position, respectively) and the validation set included 319 patients (200, 205, and 156 images of the anteroposterior, lateral, and oblique position, respectively). The quality control standard for lumbar spine x-ray radiography in this study was defined using textbook guidelines of as a reference. An enhanced encoder-decoder fully convolutional network with U-net as the backbone was implemented to segment the anatomical structures in the x-ray images. The segmentations were used to build an automatic assessment method to detect unqualified images. The dice similarity coefficient was used to evaluate segmentation performance.
Results: The dice similarity coefficient of the anteroposterior position images ranged from 0.82 to 0.96 (mean 0.91 ± 0.06); the dice similarity coefficient of the lateral position images ranged from 0.71 to 0.95 (mean 0.87 ± 0.10); the dice similarity coefficient of the oblique position images ranged from 0.66 to 0.93 (mean 0.80 ± 0.14). The accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity of the assessment method on the validation set were 0.971-0.990 (mean 0.98 ± 0.10), 0.714-0.933 (mean 0.86 ± 0.13), and 0.995-1.000 (mean 0.99 ± 0.12) for the three positions, respectively.
Conclusion: This deep learning-based algorithm achieves accurate segmentation of lumbar spine x-ray images. It provides a reliable and efficient method to identify the shape of the lumbar spine while automatically determining the radiographic image quality.
Keywords: U-net; deep learning; image segmentation; medical imaging; quality control; radiography.
Copyright © 2022 Chen, Deng, Wang, Liu, Chen, Liu, Li, Wang and Cao.
Conflict of interest statement
QW and LC were employed by Shanghai United Imaging Intelligence Co., Ltd. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
LSW-Net: Lightweight Deep Neural Network Based on Small-World properties for Spine MR Image Segmentation.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2023 Dec;58(6):1762-1776. doi: 10.1002/jmri.28735. Epub 2023 Apr 29. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2023. PMID: 37118994
-
MADR-Net: multi-level attention dilated residual neural network for segmentation of medical images.Sci Rep. 2024 Jun 3;14(1):12699. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-63538-2. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38830932 Free PMC article.
-
A Lightweight Convolutional Neural Network Based on Dynamic Level-Set Loss Function for Spine MR Image Segmentation.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2024 Apr;59(4):1438-1453. doi: 10.1002/jmri.28877. Epub 2023 Jun 29. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2024. PMID: 37382232
-
A multiple-channel and atrous convolution network for ultrasound image segmentation.Med Phys. 2020 Dec;47(12):6270-6285. doi: 10.1002/mp.14512. Epub 2020 Oct 18. Med Phys. 2020. PMID: 33007105
-
Feasibility of deep learning algorithm in diagnosing lumbar central canal stenosis using abdominal CT.Skeletal Radiol. 2025 May;54(5):947-957. doi: 10.1007/s00256-024-04796-z. Epub 2024 Sep 9. Skeletal Radiol. 2025. PMID: 39249505 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Radiation dose reduction and image quality evaluation for lateral lumbar spine projection.Heliyon. 2023 Aug 27;9(9):e19509. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e19509. eCollection 2023 Sep. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37681134 Free PMC article.
-
The Application of Artificial Intelligence in Spine Surgery: A Scoping Review.J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev. 2025 Apr 10;9(4):e24.00405. doi: 10.5435/JAAOSGlobal-D-24-00405. eCollection 2025 Apr 1. J Am Acad Orthop Surg Glob Res Rev. 2025. PMID: 40239218 Free PMC article.
-
Quality control of elbow joint radiography using a YOLOv8-based artificial intelligence technology.Eur Radiol Exp. 2024 Sep 20;8(1):107. doi: 10.1186/s41747-024-00504-7. Eur Radiol Exp. 2024. PMID: 39302546 Free PMC article.
-
A machine learning based quantification system for automated diagnosis of lumbar spondylolisthesis on spinal X-rays.Heliyon. 2024 Sep 4;10(17):e37418. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e37418. eCollection 2024 Sep 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39290282 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

