Can Neuropeptide S Be an Indicator for Assessing Anxiety in Psychiatric Disorders?
- PMID: 35558538
- PMCID: PMC9087177
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.872430
Can Neuropeptide S Be an Indicator for Assessing Anxiety in Psychiatric Disorders?
Abstract
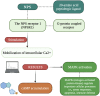
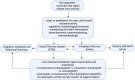
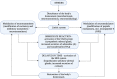
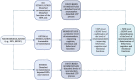
Neuropeptide S (NPS) is a neuropeptide primarily produced within three brainstem regions including locus coeruleus, trigeminal nerve nucleus, and lateral parabrachial nucleus. NPS is involved in the central regulation of stress, fear, and cognitive integration. NPS is a mediator of behavior, seeking food, and the proliferation of new adipocytes in the setting of obesity. So far, current research of NPS is only limited to animal models; data regarding its functions in humans is still scarce. Animal studies showed that anxiety and appetite might be suppressed by the action of NPS. The discovery of this neuromodulator peptide is effective considering its strong anxiolytic action, which has the potential to be an interesting therapeutic option in treating neuropsychiatric disorders. In this article, we aimed to analyze the pharmaceutical properties of NPS as well as its influence on several neurophysiological aspects-modulation of behavior, association with obesity, as well as its potential application in rehabilitation and treatment of psychiatric disorders.
Keywords: NPS; mental disorders; neurobiology; psychiatric complications; psychiatry.
Copyright © 2022 Markiewicz-Gospodarek, Kuszta, Baj, Dobrowolska and Markiewicz.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Landowski J. Neurobiology of stress. Neuropsychiatr Neuropsychol Neuropsychiatr Neuropsychol. (2007) 2:26–36.
-
- Kinalski R. Neurofizjologia kliniczna dla neurorehabilitacji. Wydawnictwo MedPharm Polska, Wrocław; (2008).
-
- Gunnar M, Vazquez D. Stress neurobiology and developmental psychopathology. Dev Psychopathol. (2015) 2:533–577. 10.1002/9780470939390.ch13 - DOI
-
- Gołyszny M. Stare i nowe neuropeptydy jako modulatory czynności osi stresu (podwzgórze-przysadka nadnercza). Varia Medica. (2018) 2:409–22. Available online at: https://journals.viamedica.pl/varia_medica/article/view/61869/46857
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

