The Influence of Sense of Place on Elementary School Students' Creativity During the COVID-19 Pandemic: The Mediating and Buffering Effects of Psychological Resilience
- PMID: 35558704
- PMCID: PMC9088518
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.775624
The Influence of Sense of Place on Elementary School Students' Creativity During the COVID-19 Pandemic: The Mediating and Buffering Effects of Psychological Resilience
Abstract
Purpose: To understand the relationship between sense of place and creativity and the mechanisms that affect this relationship, the researchers constructed a mediation model to examine the effect of sense of place on creativity and the mediating role of psychological resilience in elementary school students during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods: A total of 1,711 students in an elementary school in Beijing, China, were surveyed using Chinese-language versions of the Sense of Place Scale, the Psychological Resilience Scale-Short Version, and the Innovative Behavior Inventory. SPSS (version 23) and PROCESS plug-in (version 3.3) were used for correlation and mediation analyses.
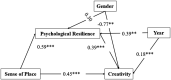
Results: (1) Correlation analysis revealed that sense of place was positively related to psychological resilience (r = 0.445, p < 0.01) and creativity (r = 0.590, p < 0.01). (2) Psychological resilience was also positively correlated with creativity (r = 0.625, p < 0.01). (3) Further, after controlling for gender and grade level, it was found that sense of place directly predicted creativity and that sense of place also indirectly predicted creativity through psychological resilience. The direct effect (0.45) and the mediating effect (0.23) accounted for 65.95 and 34.05% of the total effect, respectively.
Conclusion: The results demonstrate that sense of place is a positive predictor of creativity and can play a facilitating role to some extent. Moreover, psychological resilience is a mediating factor, acting as a buffer between sense of place and creativity. These results contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of the mechanisms influencing creativity.
Keywords: COVID-19; creativity; mediating and buffering effects; psychological resilience; sense of place.
Copyright © 2022 Xu, Wang, Zhang and Lin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Amabile T. M. (1988). A model of creativity and innovation in organizations. Res. Organ. Behav. 10, 123–167.
-
- Amabile T. M. (1996). Creativity in Context: Update to the Social Psychology of Creativity. High Ability Studies. United Kingdom: Routledge.
-
- Anser M. K., Yousaf Z., Sharif M., Yijun W., Majid A., Yasir M. (2020). Investigating employee creativity through employee polychronicity and employee resilience: A glimpse of nurses working in the health-care sector. Eur. J. Innov. Manag. 25, 39–54. doi: 10.1108/EJIM-05-2020-0176 - DOI
-
- Berg A., Hallberg I. R. (1999). Effects of systematic clinical supervision on psychiatric nurses’ sense of coherence, creativity, work-related strain, job satisfaction and view of the effects from clinical supervision: A pre-post test design. J. Psychiatr. Ment. Health Nurs. 6, 371–381. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2850.1999.00235.x, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources