Renoprotective effect of JinQi-JiangTang tablet on high-fat diet and low-dose streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic rats
- PMID: 35558809
- PMCID: PMC9091965
- DOI: 10.1039/c8ra07858k
Renoprotective effect of JinQi-JiangTang tablet on high-fat diet and low-dose streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic rats
Abstract
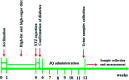
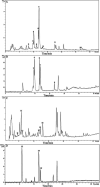
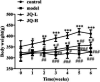
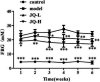
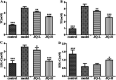
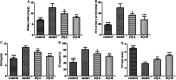
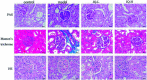
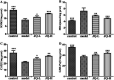
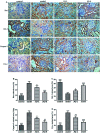
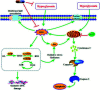
JinQi-JiangTang tablet (JQ), a traditional Chinese patent medicine, have been commonly applied to clinical therapy in type 2 diabetic patients. The present study was undertaken to investigate the renoprotective effect of JQ on type 2 diabetic rats. The type 2 diabetic rat model was successfully induced by a high-fat and high-sugar diet combined with a single low-dose of streptozotocin. Intervention with JQ could significantly diminish the body weight loss, reduce the levels of fasting blood glucose, 24 hour urinary protein, blood urea nitrogen and serum creatinine in STZ-induced diabetic rats. JQ improved the creatinine clearance in diabetic rats. What's more, the levels of total cholesterol, triglyceride and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol were markedly reduced following JQ treatment, while the level of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol was elevated. Moreover, JQ significantly improved the activity of superoxide dismutase, catalase and glutathione peroxidase, whereas decreased the level of lipid peroxidation malondialdehyde in renal tissue of diabetic rats. Furthermore, immunohistochemical analysis showed that JQ significantly downregulated the expression of Bax, Caspase-3 and Cytochrome c and upregulated Bcl-2 protein expression in the renal tissue of diabetic rats, which was considered as the major pathogeneses of apoptosis. These data demonstrated that JQ exhibited a renoprotective effect through blood glucose control, alleviating lipid metabolism, anti-oxidative stress and anti-apoptosis activities.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no conflicts of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Tuttle K. R. Bakris G. L. Bilous R. W. Chiang J. L. de Boer I. H. Goldstein-Fuchs J. Hirsch I. B. Kalantar-Zadeh K. Narva A. S. Navaneethan S. D. Neumiller J. J. Patel U. D. Ratner R. E. Whaley-Connell A. T. Molitch M. E. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2014;64:510–533. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2014.08.001. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wolf G. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2003;14:1396–1405. doi: 10.1097/01.ASN.0000065639.19190.CF. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

