Anticancer L-Asparaginase and Phytoactive Compounds From Plant Solanum nigrum Against MDR (Methicillindrug resistant) Staphylococcus aureus and Fungal Isolates
- PMID: 35558870
- PMCID: PMC9087284
- DOI: 10.1177/15593258221092379
Anticancer L-Asparaginase and Phytoactive Compounds From Plant Solanum nigrum Against MDR (Methicillindrug resistant) Staphylococcus aureus and Fungal Isolates
Abstract
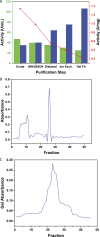
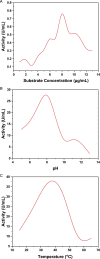
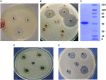
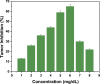
L-asparaginase is used in chemotherapy for acute lymphoblastic leukemia and other cancers. L-asparaginase derived from bacterial source triggers immune responses. The current study investigates Solanum nigrum as a novel and latent source of L-asparaginase to minimize immunological reactions. The antitumor activity of SN methanol extract was determined using the potato disc assay. InterPro Chimera and InterPro were used to predict the amino acid sequence of L-asparaginase and its anticancer activity. Purification of the enzyme was carried out to homogeneity of 1.51-fold with a recovery of 61.99%. At optimal conditions of 36.5°C, pH 8.6, and 8.5 g/mL substrate, fruit (crude extract) revealed an L-asparaginase titer of 48.23 U/mL. The molecular weight of the enzyme was calculated to be 32 ± 5 kDa using SDS PAGE. The fruit's total flavonoids and phenolic contents are 0.42 ± .030 g/mL and 94 ± 1.9 mg CAE, respectively. Anti-tumorigenic efficacy was determined to be 66% against Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Additionally, the extract possesses potent antifungal and antibacterial properties. Molecular docking provided the structural motifs and underlying interactions between L-asparaginase, N-acetylglucosamine, murine, and chitin. SN contains high levels of the enzyme L-asparaginase and phytochemicals, making it a potential source of anticancer drugs.
Keywords: L-asparaginase; Solanum nigrum; antibacterial plant; anticancer plants; antifungal plants; flavanoids; polyphenols.
© The Author(s) 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
l-Asparaginase from Solanum lycopersicum as a Nutraceutical for Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia.ACS Omega. 2024 Jan 5;9(3):3616-3624. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c07633. eCollection 2024 Jan 23. ACS Omega. 2024. PMID: 38284052 Free PMC article.
-
Bioprocessing and purification of extracellular L-asparaginase produced by endophytic Colletotrichum gloeosporioides and its anticancer activity.Prep Biochem Biotechnol. 2023;53(6):653-671. doi: 10.1080/10826068.2022.2122064. Epub 2022 Sep 22. Prep Biochem Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36137173
-
Purification, characterization, cytotoxicity and anticancer activities of L-asparaginase, anti-colon cancer protein, from the newly isolated alkaliphilic Streptomyces fradiae NEAE-82.Sci Rep. 2016 Sep 8;6:32926. doi: 10.1038/srep32926. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27605431 Free PMC article.
-
Microbial L-asparaginase: purification, characterization and applications.Arch Microbiol. 2020 Jul;202(5):967-981. doi: 10.1007/s00203-020-01814-1. Epub 2020 Feb 12. Arch Microbiol. 2020. PMID: 32052094 Review.
-
Recent developments in L-asparaginase discovery and its potential as anticancer agent.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2016 Apr;100:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2015.01.002. Epub 2015 Jan 12. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2016. PMID: 25630663 Review.
Cited by
-
Antimicrobial Activity of Rhenium Di- and Tricarbonyl Diimine Complexes: Insights on Membrane-Bound S. aureus Protein Binding.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Sep 5;15(9):1107. doi: 10.3390/ph15091107. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36145328 Free PMC article.
-
Enhanced production and purification of L-asparaginase from Bacillus paralicheniformis AUMC B-516 with potent cytotoxicity against MCF-7 cell lines.AMB Express. 2025 May 22;15(1):80. doi: 10.1186/s13568-025-01890-w. AMB Express. 2025. PMID: 40402326 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ingle AP, Wagh S, Biswas J, Mondal M, Feitosa CM, Rai M. Phyto-fabrication of different nanoparticles and evaluation of their antibacterial and anti-biofilm efficacy. Curr Nanosci. 2020;16(6):1002-1015.
-
- Van Wyk B-E, Wink M. Medicinal Plants of the World. Wallingford, UK: CABI; 2018.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

