14,15-Epoxyeicosatrienoic Acid Protect Against Glucose Deprivation and Reperfusion-Induced Cerebral Microvascular Endothelial Cells Injury by Modulating Mitochondrial Autophagy via SIRT1/FOXO3a Signaling Pathway and TSPO Protein
- PMID: 35558879
- PMCID: PMC9086968
- DOI: 10.3389/fncel.2022.888836
14,15-Epoxyeicosatrienoic Acid Protect Against Glucose Deprivation and Reperfusion-Induced Cerebral Microvascular Endothelial Cells Injury by Modulating Mitochondrial Autophagy via SIRT1/FOXO3a Signaling Pathway and TSPO Protein
Abstract
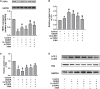
Neurovascular system plays a vital role in controlling the blood flow into brain parenchymal tissues. Additionally, it also facilitates the metabolism in neuronal biological activities. Cerebral microvascular endothelial cells (MECs) are involved in mediating progression of the diseases related to cerebral vessels, including stroke. Arachidonic acid can be transformed into epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs) under the catalysis by cytochrome P450 epoxygenase. We have reported that EETs could protect neuronal function. In our research, the further role of 14,15-EET in the protective effects of cerebral MECs and the potential mechanisms involved in oxygen glucose deprivation and reperfusion (OGD/R) were elucidated. In our study, we intervened the SIRT1/FOXO3a pathway and established a TSPO knock down model by using RNA interference technique to explore the cytoprotective role of 14,15-EET in OGD/R injury. Cerebral MECs viability was remarkably reduced after OGD/R treatment, however, 14,15-EET could reverse this effect. To further confirm whether 14,15-EET was mediated by SIRT1/FOXO3a signaling pathway and translocator protein (TSPO) protein, we also detected autophagy-related proteins, mitochondrial membrane potential, apoptosis indicators, oxygen free radicals, etc. It was found that 14,15-EET could regulate the mitophagy induced by OGD/R. SIRT1/FOXO3a signaling pathway and TSPO regulation were related to the protective role of 14,15-EET in cerebral MECs. Moreover, we also explored the potential relationship between SIRT1/FOXO3a signaling pathway and TSPO protein. Our study revealed the protective role and the potential mechanisms of 14,15-EET in cerebral MECs under OGD/R condition.
Keywords: 14; 15-EET; SIRT1/FOXO3a; TSPO; cerebrovascular disease; epoxyeicosatrienoic acids; mitophagy.
Copyright © 2022 Qu, Cao, Wang, Wang, Li and Zhu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Epoxyeicosatrienoic Acid Inhibits the Apoptosis of Cerebral Microvascular Smooth Muscle Cells by Oxygen Glucose Deprivation via Targeting the JNK/c-Jun and mTOR Signaling Pathways.Mol Cells. 2017 Nov 30;40(11):837-846. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2017.0084. Epub 2017 Oct 27. Mol Cells. 2017. PMID: 29081082 Free PMC article.
-
Notoginseng Leaf Triterpenes Ameliorates OGD/R-Induced Neuronal Injury via SIRT1/2/3-Foxo3a-MnSOD/PGC-1α Signaling Pathways Mediated by the NAMPT-NAD Pathway.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Oct 23;2020:7308386. doi: 10.1155/2020/7308386. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 33149812 Free PMC article.
-
Donepezil ameliorates oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced brain microvascular endothelial cell dysfunction via the SIRT1/FOXO3a/NF-κB pathways.Bioengineered. 2022 Mar;13(3):7760-7770. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2045833. Bioengineered. 2022. PMID: 35286233 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of inflammation on cardiovascular protective effects of cytochrome P450 epoxygenase-derived epoxyeicosatrienoic acids.Drug Metab Rev. 2014 Feb;46(1):33-56. doi: 10.3109/03602532.2013.837916. Epub 2013 Sep 16. Drug Metab Rev. 2014. PMID: 24040964 Review.
-
The Role of Epoxyeicosatrienoic Acids in Cardiac Remodeling.Front Physiol. 2021 Feb 24;12:642470. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.642470. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33716791 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The role of autophagy in brain health and disease: Insights into exosome and autophagy interactions.Heliyon. 2024 Oct 4;10(21):e38959. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e38959. eCollection 2024 Nov 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39524893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Prevent Steroid-Induced Avascular Necrosis of the Femoral Head by Modulating Cellular Autophagy.Biomedicines. 2024 Dec 12;12(12):2817. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12122817. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 39767723 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Insights Concerning Autophagy and Endothelial Cell Nitric Oxide Generation.Curr Opin Physiol. 2022 Dec;30:100614. doi: 10.1016/j.cophys.2022.100614. Epub 2022 Nov 4. Curr Opin Physiol. 2022. PMID: 40109953 Free PMC article.
-
The role of CYP-sEH derived lipid mediators in regulating mitochondrial biology and cellular senescence: implications for the aging heart.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Dec 5;15:1486717. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1486717. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39703395 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Allison S. E., Chen Y., Petrovic N., Zhang J., Bourget K., Mackenzie P. I., et al. (2017). Activation of ALDH1A1 in MDA-MB-468 breast cancer cells that over-express CYP2J2 protects against paclitaxel-dependent cell death mediated by reactive oxygen species. Biochem. Pharmacol. 143 79–89. 10.1016/j.bcp.2017.07.020 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

