Blood B Cell Depletion Reflects Immunosuppression Induced by Live-Attenuated Infectious Bursal Disease Vaccines
- PMID: 35558891
- PMCID: PMC9087897
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2022.871549
Blood B Cell Depletion Reflects Immunosuppression Induced by Live-Attenuated Infectious Bursal Disease Vaccines
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Blood B cell depletion reflects immunosuppression induced by live-attenuated infectious bursal disease vaccines.Front Vet Sci. 2023 Jun 27;10:1236998. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2023.1236998. eCollection 2023. Front Vet Sci. 2023. PMID: 37441558 Free PMC article.
Abstract
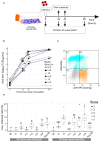
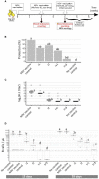
Immunosuppression in poultry production is a recurrent problem worldwide, and one of the major viral immunosuppressive agents is Infectious Bursal Disease Virus (IBDV). IBDV infections are mostly controlled by using live-attenuated vaccines. Live-attenuated Infectious Bursal Disease (IBD) vaccine candidates are classified as "mild," "intermediate," "intermediate-plus" or "hot" based on their residual immunosuppressive properties. The immunosuppression protocol described by the European Pharmacopoeia (Ph. Eur.) uses a lethal Newcastle Disease Virus (NDV) infectious challenge to measure the interference of a given IBDV vaccine candidate on NDV vaccine immune response. A Ph. Eur.-derived protocol was thus implemented to quantify immunosuppression induced by one mild, two intermediate, and four intermediate-plus live-attenuated IBD vaccines as well as a pathogenic viral strain. This protocol confirmed the respective immunosuppressive properties of those vaccines and virus. In the search for a more ethical alternative to Ph. Eur.-based protocols, two strategies were explored. First, ex vivo viral replication of those vaccines and the pathogenic strain in stimulated chicken primary bursal cells was assessed. Replication levels were not strictly correlated to immunosuppression observed in vivo. Second, changes in blood leukocyte counts in chicks were monitored using a Ph. Eur. - type protocol prior to lethal NDV challenge. In case of intermediate-plus vaccines, the drop in B cells counts was more severe. Counting blood B cells may thus represent a highly quantitative, faster, and ethical strategy than NDV challenge to assess the immunosuppression induced in chickens by live-attenuated IBD vaccines.
Keywords: B cells; IBDV; immunosuppression; live-attenuated vaccine; replication; vaccine safety.
Copyright © 2022 Courtillon, Allée, Amelot, Keita, Bougeard, Härtle, Rouby, Eterradossi and Soubies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ratcliffe MJH, Härtle S. Chapter 4 - B cells, the bursa of fabricius and the generation of antibody repertoires. In: Schat KA, Kaspers B, Kaiser P. editors. Avian Immunology. 2nd ed. Boston, MA: Academic Press; (2014). p. 65–89.
-
- Eterradossi N, Saif YM. Infectious bursal disease. In: Swayne DE, Boulianne M, Logue CM, McDougald LR, Nair V, Suarez DL. editors. Diseases of Poultry. Hoboken: Wiley-Blackwell; (2020). p. 257–83.
-
- Infectious Bursal disease (Gumboro disease) . In: Manual of Diagnostic Tests and Vaccines for Terrestrial Animals. Paris: Organisation mondiale de la santé animale; (2021). p. 931–51.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

