Construction of a Comprehensive Diagnostic Scoring Model for Prostate Cancer Based on a Novel Six-Gene Panel
- PMID: 35559023
- PMCID: PMC9086319
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.831162
Construction of a Comprehensive Diagnostic Scoring Model for Prostate Cancer Based on a Novel Six-Gene Panel
Abstract
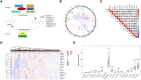
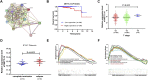
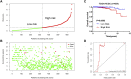
Accumulating evidence indicates that the N6-methyladenosine (m6A) modification plays a critical role in human cancers. Given the current understanding of m6A modification, this process is believed to be dynamically regulated by m6A regulators. Although the discovery of m6A regulators has greatly enhanced our understanding of the mechanism underlying m6A modification in cancers, the function and role of m6A in the context of prostate cancer (PCa) remain unclear. Here, we aimed to establish a comprehensive diagnostic scoring model that can act as a complement to prostate-specific antigen (PSA) screening. To achieve this, we first drew the landscape of m6A regulators and constructed a LASSO-Cox model using three risk genes (METTL14, HNRNP2AB1, and YTHDF2). Particularly, METTL14 expression was found to be significantly related to overall survival, tumor T stage, relapse rate, and tumor microenvironment of PCa patients, showing that it has important prognostic value. Furthermore, for the sake of improving the predictive ability, we presented a comprehensive diagnostic scoring model based on a novel 6-gene panel by combining with genes found in our previous study, and its application potential was further validated by the whole TCGA and ICGC cohorts. Our study provides additional clues and insights regarding the treatment and diagnosis of PCa patients.
Keywords: METTL14; diagnostic scoring model; m6A modification; prostate cancer; tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2022 Liu, Qiu, Sun, Xiong, Xiang and Li.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

