Description of the Molecular and Phenotypic Spectrum of Lesch-Nyhan Disease in Eight Chinese Patients
- PMID: 35559039
- PMCID: PMC9086273
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2022.868942
Description of the Molecular and Phenotypic Spectrum of Lesch-Nyhan Disease in Eight Chinese Patients
Abstract
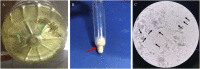
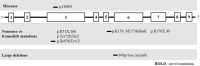
Background: Lesch-Nyhan disease (LND) is a rare disorder involving pathogenic variants in the HPRT1 gene encoding the enzyme hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRT) that result in hyperuricemia, intellectual disability, dystonic movement disorder, and compulsive self-mutilation. The purpose of the present study was to characterize the genetic basis of LND and describe its phenotypic heterogeneity by identifying the variation in the HPRT1 gene in a cohort of Chinese LND patients. Results: The median age at diagnosis was 31 mo (interquartile range (IQR): 7-76 mo), and the initial manifestations were mainly head control weakness and motor development delay. The median age of self-mutilation behavior onset was 19 mo (IQR: 17-24 mo), and all patients were required to travel in a wheelchair and fall into the predicament of compulsive self-harm behavior. There were two patients whose blood uric acid levels were normal for their high urinary acid excretion fraction without taking uric acid-lowering drugs. Seven different pathogenic variants of the HPRT1 gene were identified among eight independent pedigrees, including four novel mutations [c.299 (exon 3) T > A; loss (exon: 6) 84 bp; c.277_281delATTGC; c.468_470delGAT]. The pathogenic variant sites were mainly concentrated in exon 3, and truncating mutations (including frameshift mutations and nonsense mutations) were the most common genetic variant types (5/7, 71.4%). Conclusion: The present study described the phenotypic and molecular spectrum of LND in eight Chinese families, including four novel mutations, which expands our understanding of LND.
Keywords: HPRT1 gene; Lesch-Nyhan disease; dystonia; hyperuricemia; self-mutilation.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Qiao, Liu, Wang, Shen, Fu and Mao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Bertelli M., Randi D., Micheli V., Gallo S., Andrighetto G., Parmigiani P., et al. (2004). Molecular Basis of Hypoxanthine-Guanine Phosphoribosyltransferase Deficiency in Italian Lesch-Nyhan Patients: Identification of Nine Novel Mutations. J. Inherit. Metab. Dis. 27 (6), 767–773. 10.1023/B:BOLI.0000045799.78633.23 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

