LINC01272 activates epithelial-mesenchymal transition through miR-153-5p in Crohn's disease
- PMID: 35559411
- PMCID: PMC9091119
LINC01272 activates epithelial-mesenchymal transition through miR-153-5p in Crohn's disease
Abstract
Objectives: Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) have different functions in different diseases. There is little research on the functions of lncRNAs in Crohn's disease (CD). By using RNA-seq technology, we identified a lncRNA associated with Crohn's disease. However, the mechanism of lncRNA regulation remains unknown. This study aimed to determine the association of LINC01272 with epithelial cell-mesenchymal transition and the underlying mechanism in CD.
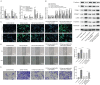
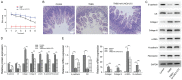
Methods: RNA was detected by qRT-PCR. The interaction of protein and RNA was determined by RNA binding protein immunoprecipitation. Luciferase reporter assays were used to detect the targeted miRNA of LINC01272. Tissue fibrosis was observed by Masson and H&E staining. Protein expression was determined by western blotting and immunofluorescence.
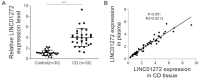
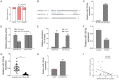
Results: LINC01272 was highly expressed in patients with CD. Knockdown of LINC01272 inhibited TGF-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Additionally, LINC01272 regulated TGF-β1-induced EMT through the miR-153-5p axis, and knockdown of LINC01272 inhibited EMT in CD mice in vivo.
Conclusion: LINC01272 activated the epithelial-mesenchymal transition through miR-153-5p in CD.
Keywords: Crohn’s disease; EMT; LINC01272; miR-153-5p.
AJTR Copyright © 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The role of long non-coding RNA in Crohn's disease.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 6;10(11):e32606. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32606. eCollection 2024 Jun 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38961978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
LINC01272/miR-876/ITGB2 axis facilitates the metastasis of colorectal cancer via epithelial-mesenchymal transition.J Cancer. 2021 May 5;12(13):3909-3919. doi: 10.7150/jca.55666. eCollection 2021. J Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34093798 Free PMC article.
-
Hsa_circRNA_102610 upregulation in Crohn's disease promotes transforming growth factor-β1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition via sponging of hsa-miR-130a-3p.World J Gastroenterol. 2020 Jun 14;26(22):3034-3055. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v26.i22.3034. World J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32587447 Free PMC article.
-
Long non-coding RNA linc00673 regulated non-small cell lung cancer proliferation, migration, invasion and epithelial mesenchymal transition by sponging miR-150-5p.Mol Cancer. 2017 Jul 11;16(1):118. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0685-9. Mol Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28697764 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA-MALAT1/miRNA-204-5p/Smad4 Axis Regulates Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition, Proliferation and Migration of Lens Epithelial Cells.Curr Eye Res. 2021 Aug;46(8):1137-1147. doi: 10.1080/02713683.2020.1857778. Epub 2020 Dec 17. Curr Eye Res. 2021. PMID: 33327804
Cited by
-
The significance of long non-coding RNAs in the pathogenesis, diagnosis and treatment of inflammatory bowel disease.Precis Clin Med. 2023 Dec 11;6(4):pbad031. doi: 10.1093/pcmedi/pbad031. eCollection 2023 Dec. Precis Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 38163004 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of long non-coding RNA in Crohn's disease.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 6;10(11):e32606. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32606. eCollection 2024 Jun 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38961978 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ChIP-Atlas 3.0: a data-mining suite to explore chromosome architecture together with large-scale regulome data.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Jul 5;52(W1):W45-W53. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae358. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38749504 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Torres J, Mehandru S, Colombel JF, Peyrin-Biroulet L. Crohn’s disease. Lancet. 2017;389:1741–1755. - PubMed
-
- Ballester Ferre MP, Bosca-Watts MM, Minguez Perez M. Crohn’s disease. Med Clin (Barc) 2018;151:26–33. - PubMed
-
- Harb WJ. Crohn’s disease of the colon, rectum, and anus. Surg Clin North Am. 2015;95:1195–1210. - PubMed
-
- Chan WPW, Mourad F, Leong RW. Crohn’s disease associated strictures. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;33:998–1008. - PubMed
-
- Li J, Mao R, Kurada S, Wang J, Lin S, Chandra J, Rieder F. Pathogenesis of fibrostenosing Crohn’s disease. Transl Res. 2019;209:39–54. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
