Anxiety and depression in graduating university students during the COVID-19 pandemic: a longitudinal study
- PMID: 35559421
- PMCID: PMC9091131
Anxiety and depression in graduating university students during the COVID-19 pandemic: a longitudinal study
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the prevalence of anxiety and depression in graduating university students during the COVID-19 pandemic and determine the associated factors.
Methods: A total of 681 graduating university students and 620 juniors enrolled in the first stage. The Self-rating Anxiety Scale (SAS) and Self-rating Depression Scale (SDS) were used to measure anxiety and depression. In the second stage, 578 of the 681 graduating students completed the SAS and SDS questionnaires after graduation.
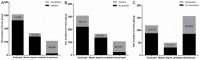
Results: The average SAS score of the graduating university students was significantly higher than that of the juniors (47.66±12.86 vs. 43.97±10.42, P<0.001). Depression was more prevalent among the graduating university students than in the control groups (39.06% vs. 9.19%, P<0.01). The percentages of anxiety and depression significantly decreased after graduation (t=8.602, P<0.001). The anxiety of graduating university students was associated with gender (OR=1.62, 95% CI: 1.10-2.37), monthly family income (OR=0.05, 95% CI: 0.02-0.11), and weekly exercise time (OR=0.53, 95% CI: 0.35-0.08). Their depression was related to their family's monthly income (OR=0.09, 95% CI: 0.05-0.16) and father's educational status (OR=2.24, 95% CI: 1.17-4.30).
Conclusion: Anxiety and depression were rife within the graduating Chinese university students during the period of the COVID-19 pandemic and were both associated with monthly family income. Treatments tailored to specific targets are needed for graduating university students with mental problems.
Keywords: COVID-19 pandemic; Graduating university students; anxiety; depression.
AJTR Copyright © 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
References
-
- Bayram N, Bilgel N. The prevalence and socio-demographic correlations of depression, anxiety and stress among a group of university students. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol. 2008;43:667–672. - PubMed
-
- Çelik N, Ceylan B, Ünsal A, Çağan Ö. Depression in health college students: relationship factors and sleep quality. Psychol Health Med. 2019;24:625–630. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources