Ripk3 signaling regulates HSCs during stress and represses radiation-induced leukemia in mice
- PMID: 35561683
- PMCID: PMC9213819
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2022.04.009
Ripk3 signaling regulates HSCs during stress and represses radiation-induced leukemia in mice
Abstract
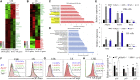
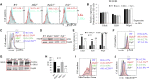
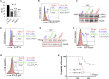
Receptor-interacting protein kinase 3 (Ripk3) is one of the critical mediators of inflammatory cytokine-stimulated signaling. Here we show that Ripk3 signaling selectively regulates both the number and the function of hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) during stress conditions. Ripk3 signaling is not required for normal homeostatic hematopoiesis. However, in response to serial transplantation, inactivation of Ripk3 signaling prevents stress-induced HSC exhaustion and functional HSC attenuation, while in response to fractionated low doses of ionizing radiation (IR), inactivation of Ripk3 signaling accelerates leukemia/lymphoma development. In both situations, Ripk3 signaling is primarily stimulated by tumor necrosis factor-α. Activated Ripk3 signaling promotes the elimination of HSCs during serial transplantation and pre-leukemia stem cells (pre-LSCs) during fractionated IR by inducing Mlkl-dependent necroptosis. Activated Ripk3 signaling also attenuates HSC functioning and represses a pre-LSC-to-LSC transformation by promoting Mlkl-independent senescence. Furthermore, we demonstrate that Ripk3 signaling induces senescence in HSCs and pre-LSCs by attenuating ISR-mediated mitochondrial quality control.
Keywords: HSCs; Mlkl; Ripk3; ionizing radiation; leukemia; necroptosis.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Boniver J., Humblet C., Defresne M.P. Tumor necrosis factor and interferon gamma inhibit the development of radiation-induced thymic lymphomas in C57BL/Ka mice. Leukemia. 1989;3:611–613. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

