Breast cancer larger than 2.5 cm with tumor-free radioisotope-hot sentinel nodes has higher risk of non-hot axillary lymph node metastasis
- PMID: 35562283
- PMCID: PMC9250121
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bj.2021.04.009
Breast cancer larger than 2.5 cm with tumor-free radioisotope-hot sentinel nodes has higher risk of non-hot axillary lymph node metastasis
Abstract
Background: Sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) is the standard axillary staging approach for early breast cancer with clinically negative axillary involvement. Adequate SLNB should include the removal of not only radioactive tracer-labeled lymph nodes (hot nodes or SLNs) but also suspicious unlabeled nodes (non-hot nodes or non-SLNs). However, the biopsy of non-hot nodes is highly dependent on the surgeons' experiences. This article aims to facilitate the surgeon's decision making by elucidating parameters that correlate with non-hot node metastasis.
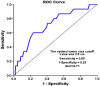
Methods: From 2013 to 2016, clinically node-negative (cN0) breast cancer patients receiving axillary SLNB using single Tc-99m tracer method at our institute were recruited. Patients were excluded if they had received prior neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Among them, cases that have at least one non-isotope-hot node biopsied were retrospectively reviewed with a particular focus on patients with pathologically negative isotope-hot SLNs. The correlation of clinicopathological data with metastasis to axillary lymph nodes and sentinel lymph nodes was analyzed with the Chi-squared test, Fisher's exact test, and multivariate logistic regression. Receiver operating curve (ROC) was applied for continuous variables that predicted non-hot node metastasis; relapse-free survival (RFS) and locoregional relapse-free survival (LRRFS) were compared by Kaplan-Meier analysis.
Results: In 632 isotope-hot SLN negative patients, T stage showed a correlation with non-isotope-hot SLN metastasis (p = 0.035, odds ratio (OR) 9.65). Tumors larger than 2.5 cm best predict non-isotope-hot SLN metastasis (area under curve (AUC) = 0.71). With a median follow up of 41.80 months, locoregional relapse-free survival was significantly worse in cases with non-hot node metastasis (66.2% vs. 69.0%, p = 0.001).
Conclusion: In the setting of SLNB using single radioisotope tracer, non-hot node metastasis in cases with negative hot SLN still carries a higher locoregional recurrence rate (13.3%). For early breast cancer larger than 2.5 cm, removal of suspicious non-hot nodes should be included for a precision therapy.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Lymphovascular invasion; Sentinel lymph node; Sentinel lymph node biopsy; Tumor size.
Copyright © 2021 Chang Gung University. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Positive non-sentinel axillary lymph nodes in breast cancer with 1-2 sentinel lymph node metastases.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Nov;97(44):e13015. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000013015. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30383658 Free PMC article.
-
Clinicopathologic analysis of sentinel lymph node mapping in early breast cancer.Breast J. 2003 May-Jun;9(3):153-62. doi: 10.1046/j.1524-4741.2003.09304.x. Breast J. 2003. PMID: 12752622
-
De-Escalating the Extent of Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in Patients With Ductal Carcinoma in Situ Undergoing Mastectomy.Clin Breast Cancer. 2024 Dec;24(8):716-720. doi: 10.1016/j.clbc.2024.08.012. Epub 2024 Aug 23. Clin Breast Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39261257
-
Lymphovascular invasion is a significant risk factor for non-sentinel nodal metastasis in breast cancer patients with sentinel lymph node (SLN)-positive breast cancer: a cross-sectional study.World J Surg Oncol. 2023 Dec 14;21(1):386. doi: 10.1186/s12957-023-03273-6. World J Surg Oncol. 2023. PMID: 38097994 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Accuracy of CEUS-guided sentinel lymph node biopsy in early-stage breast cancer: a study review and meta-analysis.World J Surg Oncol. 2020 May 29;18(1):112. doi: 10.1186/s12957-020-01890-z. World J Surg Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32471428 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
What makes tics tick? Insights into Tourette syndrome.Biomed J. 2022 Apr;45(2):219-226. doi: 10.1016/j.bj.2022.04.004. Epub 2022 Apr 20. Biomed J. 2022. PMID: 35460927 Free PMC article.
-
Combined Fluorescein and Methylene Blue Dye for Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy in Patients of Early Carcinoma Breast: A Promising Technique.Indian J Surg Oncol. 2024 Dec;15(4):891-900. doi: 10.1007/s13193-024-01976-0. Epub 2024 Jul 4. Indian J Surg Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39555376
References
-
- Liao G.-S., Hsu H.-M., Chu C.-H., Hong Z.-J., Fu C.-Y., Chou Y.-C., et al. Prognostic role of lymphovascular invasion and lymph node status among breast cancer subtypes. J Med Sci. 2018;38:54–61.
-
- Raut C.P., Hunt K.K., Akins J.S., Daley M.D., Ross M.I., Singletary S.E., et al. Incidence of anaphylactoid reactions to isosulfan blue dye during breast carcinoma lymphatic mapping in patients treated with preoperative prophylaxis: results of a surgical prospective clinical practice protocol. Cancer. 2005;104:692–699. - PubMed
-
- Cimmino V.M., Brown A.C., Szocik J.F., Pass H.A., Moline S., De S.K., et al. Allergic reactions to isosulfan blue during sentinel node biopsy--a common event. Surgery. 2001;130:439–442. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

