Disciplinary processes for nurses, from organizational supervision to outcomes: A document analysis of a regulatory authority's decisions
- PMID: 35562646
- PMCID: PMC10084253
- DOI: 10.1111/jonm.13679
Disciplinary processes for nurses, from organizational supervision to outcomes: A document analysis of a regulatory authority's decisions
Abstract
Aim: This study aims to explore the disciplinary processes for nurses, from organizational supervision to final decisions by the Finnish regulatory authority.
Background: Regulatory authorities are responsible for protecting the public, by ensuring that they receive safe, competent and ethical nursing care, but little is known about the disciplinary processes for nurses.
Methods: This is a retrospective document analysis of 296 disciplinary decisions by the Finnish regulatory authority from 2007 to 2016. The data were analysed using a quantitative design with descriptive statistics.
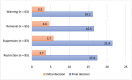
Results: We studied 204 disciplined nurses (81.4% female) with a mean age of 43.5 years. The disciplinary process comprised organizational supervision, complaints, investigations and decisions. Nurses with substance abuse issues were more likely to face criminal investigations and receive temporary decisions. The process lasted from under 1 month to years and could have profound effects on nurses, colleagues and nurse managers and compromise patient safety.
Conclusion: This study identified key factors that could inform the disciplinary processes for nurses. More knowledge is needed about how organisations ensure patient safety when unprofessional conduct is suspected.
Implications for nursing management: Retaining nursing professionals is vital due to global shortages, and more attention should be paid to organizational supervision and support for nurses during disciplinary processes.
Keywords: complaints; disciplinary action; nursing management; professional regulations; registered nurses.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Nursing Management published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest declare.
Figures
References
-
- Azuri, P. , Haron, Y. , Riba, S. , & Sar‐Lev, S. (2014). Disciplinary procedures against Israeli nurses. Journal of Nursing Regulation, 4(4), 51–56. 10.1016/S2155-8256(15)30117-4 - DOI
-
- Balestra, M. (2012). The best defense for registered nurses and nurse practitioners: Understanding the disciplinary process. Journal of Nursing Law, 15(2), 39–44. 10.1891/1073-7472.15.2.39 - DOI
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources