Resolution of Inflammation in Retinal Disorders: Briefly the State
- PMID: 35562891
- PMCID: PMC9100636
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23094501
Resolution of Inflammation in Retinal Disorders: Briefly the State
Abstract
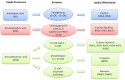
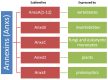
The most frequent retinal diseases, such as diabetic retinopathy, age-related macular degeneration and posterior uveitis, are underlined by oxidative stress or aging-induced retinal inflammation, which contributes to vision impairing or loss. Resolution of inflammation is emerging as a critical phase able to counteract the inflammatory process leading to the progression of retinal damage. Particularly, pro-resolving mediators (PMs) play a key role in the modulation of inflammatory exudates and could be considered a new target to be investigated in different inflammatory-autoimmune pathologies. Here, we highlight the most recent studies concerning the role of the main PMs (lipoxins, resolvins, prtectins, maresins and annexins) in retinal inflammation, in order to collect the best evidence in the field of inflammatory retinal damage resolution and to propose novel pharmacological approaches in the management of the most common retinal diseases.
Keywords: annexins; galectins; inflammation; lipoxins; maresins; pro-resolving mediators; protectins; resolvins; retinopathy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical