Crosstalk between β-Catenin and CCL2 Drives Migration of Monocytes towards Glioblastoma Cells
- PMID: 35562953
- PMCID: PMC9101913
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23094562
Crosstalk between β-Catenin and CCL2 Drives Migration of Monocytes towards Glioblastoma Cells
Abstract
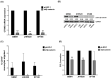
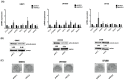
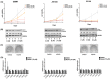
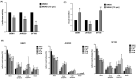
Isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH)-wildtype glioblastoma (GBM) is a fast growing and highly heterogeneous tumor, often characterized by the presence of glioblastoma stem cells (GSCs). The plasticity of GSCs results in therapy resistance and impairs anti-tumor immune response by influencing immune cells in the tumor microenvironment (TME). Previously, β-catenin was associated with stemness in GBM as well as with immune escape mechanisms. Here, we investigated the effect of β-catenin on attracting monocytes towards GBM cells. In addition, we evaluated whether CCL2 is involved in β-catenin crosstalk between monocytes and tumor cells. Our analysis revealed that shRNA targeting β-catenin in GBMs reduces monocytes attraction and impacts CCL2 secretion. The addition of recombinant CCL2 restores peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) migration towards medium (TCM) conditioned by shβ-catenin GBM cells. CCL2 knockdown in GBM cells shows similar effects and reduces monocyte migration to a similar extent as β-catenin knockdown. When investigating the effect of CCL2 on β-catenin activity, we found that CCL2 modulates components of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and alters the clonogenicity of GBM cells. In addition, the pharmacological β-catenin inhibitor MSAB reduces active β-catenin, downregulates the expression of associated genes and alters CCL2 secretion. Taken together, we showed that β-catenin plays an important role in attracting monocytes towards GBM cells in vitro. We hypothesize that the interactions between β-catenin and CCL2 contribute to maintenance of GSCs via modulating immune cell interaction and promoting GBM growth and recurrence.
Keywords: CCL2; GSCs; MSAB; Wnt; glioblastoma; immune evasion; monocytes; β-catenin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Stupp R., Hegi M.E., Mason W.P., Van Den Bent M.J., Taphoorn M.J., Janzer R.C., Ludwin S.K., Allgeier A., Fisher B., Belanger K., et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009;10:459–466. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70025-7. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

