Enhanced cGMP Interactor Rap Guanine Exchange Factor 4 (EPAC2) Expression and Activity in Degenerating Photoreceptors: A Neuroprotective Response?
- PMID: 35563009
- PMCID: PMC9103912
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23094619
Enhanced cGMP Interactor Rap Guanine Exchange Factor 4 (EPAC2) Expression and Activity in Degenerating Photoreceptors: A Neuroprotective Response?
Abstract
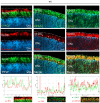
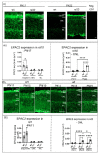
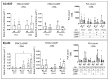
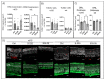
The disease retinitis pigmentosa (RP) leads to photoreceptor degeneration by a yet undefined mechanism(s). In several RP mouse models (i.e., rd mice), a high cyclic GMP (cGMP) level within photoreceptors is detected, suggesting that cGMP plays a role in degeneration. The rap guanine exchange factor 4 (EPAC2) is activated by cyclic AMP (cAMP) and is an accepted cGMP-interacting protein. It is unclear whether and how cGMP interacts with EPAC2 in degenerating photoreceptors; we therefore investigated EPAC2 expression and interactions with cGMP and cAMP in retinas of the rd1 and rd10 models for retinal degeneration. EPAC2 expression in the photoreceptor layer increased significantly during rd1 and rd10 degeneration, and an increase in EPAC2 interactions with cGMP but not cAMP in the rd1 was also seen via a proximity ligation assay on histological sections. Retinal explant cultures revealed that pharmacological inhibition of the EPAC2 activity reduced the photoreceptor layer thickness in the rd10 retina, suggesting that EPAC2 inhibition promotes degeneration. Taken together, our results support the hypothesis that high degeneration-related cGMP leads to increased EPAC2 and cGMP interactions, inhibiting EPAC2. By inference, EPAC2 could have neuroprotective capacities that may be exploited in the future.
Keywords: cAMP; cGMP; neuroprotective; photoreceptors; rap guanine exchange factor 4; retinal degeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
F.S. is employed at Biolog Life Science Institute GmbH & Co. KG, which offers the analogs and other products used in this study on a commercial basis.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The cGMP system in normal and degenerating mouse neuroretina: New proteins with cGMP interaction potential identified by a proteomics approach.J Neurochem. 2021 Jun;157(6):2173-2186. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15251. Epub 2020 Dec 5. J Neurochem. 2021. PMID: 33230839 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of cGMP-Dependent Photoreceptor Cytotoxicity With Mycophenolate Is Neuroprotective in Murine Models of Retinitis Pigmentosa.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020 Aug 3;61(10):25. doi: 10.1167/iovs.61.10.25. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020. PMID: 32785677 Free PMC article.
-
Exogenous PDE5 Expression Rescues Photoreceptors in RD1 Mice.Curr Med Chem. 2022;29(40):6115-6124. doi: 10.2174/0929867329666220216111952. Curr Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 35170405
-
Do cGMP Levels Drive the Speed of Photoreceptor Degeneration?Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1074:327-333. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-75402-4_40. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 29721960 Review.
-
The cGMP Pathway and Inherited Photoreceptor Degeneration: Targets, Compounds, and Biomarkers.Genes (Basel). 2019 Jun 14;10(6):453. doi: 10.3390/genes10060453. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31207907 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chemical signaling in the developing avian retina: Focus on cyclic AMP and AKT-dependent pathways.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Dec 9;10:1058925. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.1058925. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36568967 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Retinitis Pigmentosa: Novel Therapeutic Targets and Drug Development.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Feb 17;15(2):685. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15020685. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36840007 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multiple Roles of cAMP in Vertebrate Retina.Cells. 2023 Apr 14;12(8):1157. doi: 10.3390/cells12081157. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37190066 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fahim A.T., Daiger S.P., Weleber R.G. Nonsyndromic Retinitis Pigmentosa Overview. GeneReviews®. [(accessed on 23 September 2020)]; Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20301590.
-
- Petit L., Lhériteau E., Weber M., Le Meur G., Deschamps J.Y., Provost N., Mendes-Madeira A., Libeau L., Guihal C., Colle M.A., et al. Restoration of vision in the PDE6β-deficient dog, a large animal model of rod-cone dystrophy. Mol. Ther. 2012;20:2019–2030. doi: 10.1038/mt.2012.134. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 765441/European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under the Marie Sklodowska-Curie
- N/A/Stiftelsen för Synskadade i f.d. Malmöhus län
- N/A/Kronprinsessan Margaretas Arbetsnämnd för synskadade
- N/A/Ögonfonden
- N/A/The Royal Physiographic Society of Lund - the Natural Sciences, Medicine and Tech-nology - Medicine
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

