MicroRNA Alteration, Application as Biomarkers, and Therapeutic Approaches in Neurodegenerative Diseases
- PMID: 35563107
- PMCID: PMC9104163
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23094718
MicroRNA Alteration, Application as Biomarkers, and Therapeutic Approaches in Neurodegenerative Diseases
Abstract
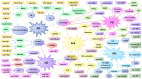
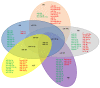
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are essential post-transcriptional gene regulators involved in various neuronal and non-neuronal cell functions and play a key role in pathological conditions. Numerous studies have demonstrated that miRNAs are dysregulated in major neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, or Huntington's disease. Hence, in the present work, we constructed a comprehensive overview of individual microRNA alterations in various models of the above neurodegenerative diseases. We also provided evidence of miRNAs as promising biomarkers for prognostic and diagnostic approaches. In addition, we summarized data from the literature about miRNA-based therapeutic applications via inhibiting or promoting miRNA expression. We finally identified the overlapping miRNA signature across the diseases, including miR-128, miR-140-5p, miR-206, miR-326, and miR-155, associated with multiple etiological cellular mechanisms. However, it remains to be established whether and to what extent miRNA-based therapies could be safely exploited in the future as effective symptomatic or disease-modifying approaches in the different human neurodegenerative disorders.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease (AD); Huntington’s disease (HD); Parkinson’s disease (PD); amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS); biomarker; dysregulation; microRNAs (miRNAs); multiple sclerosis (MS); neurodegenerative diseases.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
microRNAs and Neurodegenerative Diseases.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;888:85-105. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-22671-2_6. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 26663180 Review.
-
Shared miRNA landscapes of COVID-19 and neurodegeneration confirm neuroinflammation as an important overlapping feature.Front Mol Neurosci. 2023 Mar 17;16:1123955. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2023.1123955. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37008787 Free PMC article.
-
miRNAs as biomarkers of neurodegenerative disorders.Biomark Med. 2017 Feb;11(2):151-167. doi: 10.2217/bmm-2016-0242. Epub 2017 Jan 26. Biomark Med. 2017. PMID: 28125293 Review.
-
MicroRNA (miRNA) as a biomarker for diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutics molecules in neurodegenerative disease.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Aug;177:116899. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116899. Epub 2024 Jun 17. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 38889636 Review.
-
Current Updates on the Role of MicroRNA in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases.Curr Gene Ther. 2024;24(2):122-134. doi: 10.2174/0115665232261931231006103234. Curr Gene Ther. 2024. PMID: 37861022 Review.
Cited by
-
Harnessing the Stem Cell Niche in Regenerative Medicine: Innovative Avenue to Combat Neurodegenerative Diseases.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 12;25(2):993. doi: 10.3390/ijms25020993. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38256066 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel therapeutic targets to halt the progression of Parkinson's disease: an in-depth review on molecular signalling cascades.3 Biotech. 2023 Jul;13(7):218. doi: 10.1007/s13205-023-03637-5. Epub 2023 May 30. 3 Biotech. 2023. PMID: 37265542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miR-153 promotes neural differentiation by activating the cell adhesion/Ca2+ signaling pathway and targeting ion channel activity in HT-22 cells by bioinformatic analysis.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 26;10(9):e30204. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e30204. eCollection 2024 May 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38694121 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicles: biological mechanisms and emerging therapeutic opportunities in neurodegenerative diseases.Transl Neurodegener. 2024 Dec 6;13(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s40035-024-00453-6. Transl Neurodegener. 2024. PMID: 39643909 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plasma microRNA Signature as Companion Diagnostic for Abiraterone Acetate Treatment in Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: A Pilot Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 21;25(11):5573. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115573. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38891761 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous