Novel Bacillus ginsengihumi CMRO6 Inhibits Adipogenesis via p38MAPK/Erk44/42 and Stimulates Glucose Uptake in 3T3-L1 Pre-Adipocytes through Akt/AS160 Signaling
- PMID: 35563118
- PMCID: PMC9104516
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms23094727
Novel Bacillus ginsengihumi CMRO6 Inhibits Adipogenesis via p38MAPK/Erk44/42 and Stimulates Glucose Uptake in 3T3-L1 Pre-Adipocytes through Akt/AS160 Signaling
Abstract
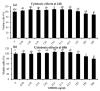
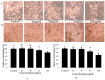
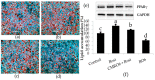
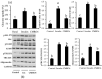
The health benefits of probiotics have been known for decades, but there has only been limited use of probiotics in the treatment of obesity. In this study, we describe, for the first time, the role of cell-free metabolites (CM) from Bacillus ginsengihumi-RO6 (CMRO6) in adipogenesis and lipogenesis in 3T3-L1 pre-adipocytes. The experimental results show that CMRO6 treatment effectively reduced lipid droplet accumulation and the expression of CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein α and β (C/EBPα and C/EBPβ), peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPAR-γ), serum regulatory binding protein 1c (SREBP-1c), fatty acid-binding protein 4 (FABP4), fatty acid synthase (FAS), acetyl CoA carboxylase (ACC), phosphorylated p38MAPK, and Erk44/42. Additionally, CMRO6 treatment significantly increased glucose uptake and phosphorylated Akt (S473), AS160, and TBC1D1 protein expressions. Considering the results of this study, B. ginsengihumi may be a novel probiotic used for the treatment of obesity and its associated metabolic disorders.
Keywords: 3T3-L1; Bacillus ginsengihumi; cell-free metabolites; glucose uptake; lipid; probiotic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Leuconostoc Citreum Inhibits Adipogenesis and Lipogenesis by Inhibiting p38 MAPK/Erk 44/42 and Stimulating AMPKα Signaling Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 17;24(8):7367. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087367. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108530 Free PMC article.
-
Saikosaponin A and D Inhibit Adipogenesis via the AMPK and MAPK Signaling Pathways in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 22;22(21):11409. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111409. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34768840 Free PMC article.
-
Derhamnosylmaysin Inhibits Adipogenesis via Inhibiting Expression of PPARγ and C/EBPα in 3T3-L1 Cells.Molecules. 2022 Jun 30;27(13):4232. doi: 10.3390/molecules27134232. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35807476 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of natural alkaloid bouchardatine as a novel inhibitor of adipogenesis/lipogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes.Bioorg Med Chem. 2015 Aug 1;23(15):4719-4727. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2015.05.057. Epub 2015 Jun 5. Bioorg Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 26088335
-
Vanadium(IV)-chlorodipicolinate inhibits 3T3-L1 preadipocyte adipogenesis by activating LKB1/AMPK signaling pathway.J Inorg Biochem. 2016 Sep;162:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2016.06.013. Epub 2016 Jun 5. J Inorg Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27318173
Cited by
-
A Thai Traditional Triple-Fruit Formulation "Phikud Tri-Phon" May Provide Fat Loss and Nutritional Benefits.Foods. 2022 Oct 2;11(19):3067. doi: 10.3390/foods11193067. Foods. 2022. PMID: 36230143 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of Plocamium telfairiae Extract-Functionalized Au Nanostructures and Their Anti-Adipogenic Activity through PLD1.Mar Drugs. 2022 Jun 27;20(7):421. doi: 10.3390/md20070421. Mar Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35877714 Free PMC article.
-
Leuconostoc Citreum Inhibits Adipogenesis and Lipogenesis by Inhibiting p38 MAPK/Erk 44/42 and Stimulating AMPKα Signaling Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 17;24(8):7367. doi: 10.3390/ijms24087367. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37108530 Free PMC article.
-
Role of bariatric surgery in improving diabetic cardiomyopathy: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives (Review).Mol Med Rep. 2024 Nov;30(5):199. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2024.13323. Epub 2024 Sep 6. Mol Med Rep. 2024. PMID: 39239741 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dihydro-Resveratrol Attenuates Oxidative Stress, Adipogenesis and Insulin Resistance in In Vitro Models and High-Fat Diet-Induced Mouse Model via AMPK Activation.Nutrients. 2023 Jun 30;15(13):3006. doi: 10.3390/nu15133006. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37447331 Free PMC article.
References
-
- WHO . Obesity: Preventing and Managing the Global Epidemic. World Health Organization; Geneva, Switzerland: 2000. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

